RNA-Seq Analysis of Protection against Chronic Alcohol Liver Injury by Rosa roxburghii Fruit Juice (Cili) in Mice
- PMID: 35565941
- PMCID: PMC9104053
- DOI: 10.3390/nu14091974
RNA-Seq Analysis of Protection against Chronic Alcohol Liver Injury by Rosa roxburghii Fruit Juice (Cili) in Mice
Abstract
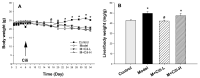
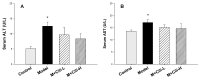
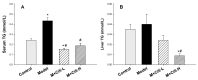
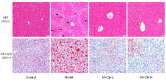
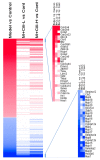
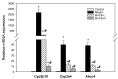
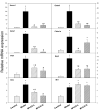
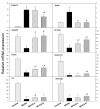
Rosa roxburghii Tratt. fruit juice (Cili) is used as a medicinal and edible resource in China due to its antioxidant and hypolipidemic potentials. The efficacy of Cili in protecting alcohol-induced liver injury and its underlying mechanism was investigated. C57BL/6J mice received a Lieber-DeCarli liquid diet containing alcohol to produce liver injury. After the mice were adapted gradually to 5% alcohol, Cili (4 mL and 8 mL/kg/day for 4 weeks) were gavaged for treatment. The serum enzyme activities, triglyceride levels, histopathology and Oil-red O staining were examined. The RNA-Seq and qPCR analyses were performed to determine the protection mechanisms. Cili decreased serum and liver triglyceride levels in mice receiving alcohol. Hepatocyte degeneration and steatosis were improved by Cili. The RNA-Seq analyses showed Cili brought the alcohol-induced aberrant gene pattern towards normal. The qPCR analysis verified that over-activation of CAR and PXR (Cyp2a4, Cyp2b10 and Abcc4) was attenuated by Cili. Cili alleviated overexpression of oxidative stress responsive genes (Hmox1, Gsta1, Gstm3, Nqo1, Gclc, Vldlr, and Cdkn1a), and rescued alcohol-downregulated metabolism genes (Angptl8, Slc10a2, Ces3b, Serpina12, C6, and Selenbp2). Overall, Cili was effective against chronic alcohol liver injury, and the mechanisms were associated with decreased oxidative stress, improved lipid metabolism through modulating nuclear receptor CAR-, PXR-and Nrf2-mediated pathways.
Keywords: Oil-red O staining; RNA-Seq; Rosa roxburghii Tratt. fruit juice (Cili); chronic alcohol liver injury; qPCR; triglyceride.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Protective effects of fermented Rosa roxburghii Tratt juice against ethanol‑induced hepatocyte injury by regulating the NRF2‑AMPK signaling pathway in AML‑12 cells.Mol Med Rep. 2024 Oct;30(4):174. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2024.13298. Epub 2024 Aug 2. Mol Med Rep. 2024. PMID: 39092554 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome Analysis of Protection by Dendrobium Nobile Alkaloids (DNLA) against Chronic Alcoholic Liver Injury in Mice.Biomedicines. 2022 Nov 3;10(11):2800. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10112800. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 36359319 Free PMC article.
-
Prevention of high-fat/high-sugar diet-induced type 2 diabetes mellitus-associated non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in rats with fermented and raw Rosa roxburghii Tratt (Cili) juice.Front Nutr. 2025 May 19;12:1584551. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1584551. eCollection 2025. Front Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40458826 Free PMC article.
-
Physicochemical, biological properties, and flavour profile of Rosa roxburghii Tratt, Pyracantha fortuneana, and Rosa laevigata Michx fruits: A comprehensive review.Food Chem. 2022 Jan 1;366:130509. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.130509. Epub 2021 Jul 1. Food Chem. 2022. PMID: 34339923 Review.
-
Recent advances in polysaccharides from Rose roxburghii Tratt fruits: isolation, structural characterization, and bioactivities.Food Funct. 2022 Dec 13;13(24):12561-12571. doi: 10.1039/d2fo02192g. Food Funct. 2022. PMID: 36453451 Review.
Cited by
-
Protective effects of fermented Rosa roxburghii Tratt juice against ethanol‑induced hepatocyte injury by regulating the NRF2‑AMPK signaling pathway in AML‑12 cells.Mol Med Rep. 2024 Oct;30(4):174. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2024.13298. Epub 2024 Aug 2. Mol Med Rep. 2024. PMID: 39092554 Free PMC article.
-
The Phytochemical Characterization of a Cili (Rosa roxburghii) Fruit Low-Temperature Extract with Hepatoprotective Effects.Foods. 2025 Apr 9;14(8):1301. doi: 10.3390/foods14081301. Foods. 2025. PMID: 40282703 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomic analysis of mouse liver lesions at all three stages of Echinococcus granulosus infection.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2024 Dec 3;18(12):e0012659. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0012659. eCollection 2024 Dec. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2024. PMID: 39625960 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the Prevention of Lipid Deposition Caused by High-Fat Diet and Its Mechanism of Action of Rosa roxburghii Fermented Juice Based on Liver Metabolomics and Gut Microbiota.Food Sci Nutr. 2025 Jul 28;13(8):e70449. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.70449. eCollection 2025 Aug. Food Sci Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40735404 Free PMC article.
-
The effect and mechanism of Germacrone in ameliorating alcoholic fatty liver by inhibiting Nrf2/Rbp4.Chin Med. 2025 May 29;20(1):77. doi: 10.1186/s13020-025-01132-y. Chin Med. 2025. PMID: 40442809 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Committee Z.B.E. Zhonghua Bencao. Guizhou Science and Technology Press; Guiyang, China: 2005. pp. 334–335.
-
- Pharmacopoeia . Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China. Volume 1 Chinese Medical Press; Beijing, China: 2020.
-
- Wang L.T., Lv M.J., An J.Y., Fan X.H., Dong M.Z., Zhang S.D., Wang J.D., Wang Y.Q., Cai Z.H., Fu Y.J. Botanical characteristics, phytochemistry and related biological activities of Rosa roxburghii Tratt fruit, and its potential use in functional foods: A review. Food Funct. 2021;12:1432–1451. doi: 10.1039/D0FO02603D. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

