Mechanistic Insights into the Ameliorating Effect of Melanogenesis of Psoralen Derivatives in B16F10 Melanoma Cells
- PMID: 35565964
- PMCID: PMC9102055
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27092613
Mechanistic Insights into the Ameliorating Effect of Melanogenesis of Psoralen Derivatives in B16F10 Melanoma Cells
Abstract
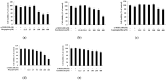
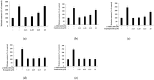
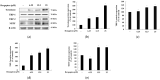
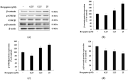
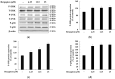
The objectives of this study were to investigate the melanogenetic potential of the psoralen derivatives 5-hydroxypsoralen, 5-methoxypsoralen, 8-hydroxypsoralen, 8-methoxypsoralen, and 5,8-dimethoxypsoralen in B16F10 melanoma cells. The results indicated that melanin production is significantly stimulated in B16F10 melanoma cells with 5-methoxypsoralen, 8-methoxypsoralen, and 5,8-dimethoxypsoralen, especially for 5-methoxypsoralen (bergapten), as reported previously. In addition, Western blot results showed that the protein levels of microphthalmia-associated transcription factor (MITF), tyrosinase, tyrosinase-related protein-1 (TRP-1), and tyrosinase-related protein-2 (TRP-2) increase after bergapten treatment for the first time. The results also showed that bergapten promotes the phosphorylation of Akt at Ser 473 and glycogen synthase kinase-3β at Ser 9. Moreover, bergapten increased the content of β-catenin in the cell cytoplasm and nucleus by reducing the phosphorylated β-catenin (p-β-catenin) content. The results also indicated that bergapten regulates melanogenesis by upregulating the phosphorylation of p38 and JNK-mitogen-activated protein kinase. Taken together, these findings suggest that the regulation of melanogenesis by bergapten may be mediated by the β-catenin and MAPK signaling pathways and that bergapten might provide new insights into the pathogenesis of pigmented diseases.
Keywords: 5,8-dimethoxypsoralen; 5-hydroxypsoralen; 5-methoxypsoralen; 8-hydroxypsoralen; 8-methoxypsoralen; MAPK; β-catenin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

