Cupressus sempervirens Essential Oil: Exploring the Antibacterial Multitarget Mechanisms, Chemcomputational Toxicity Prediction, and Safety Assessment in Zebrafish Embryos
- PMID: 35565980
- PMCID: PMC9103706
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27092630
Cupressus sempervirens Essential Oil: Exploring the Antibacterial Multitarget Mechanisms, Chemcomputational Toxicity Prediction, and Safety Assessment in Zebrafish Embryos
Abstract
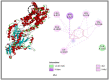
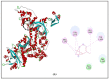
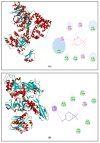
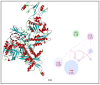
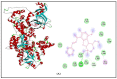
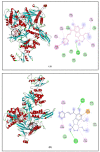
Nowadays, increasing interest has recently been given to the exploration of new food preservatives to avoid foodborne outbreaks or food spoilage. Likewise, new compounds that substitute the commonly used synthetic food preservatives are required to restrain the rising problem of microbial resistance. Accordingly, the present study was conducted to examine the chemical composition and the mechanism(s) of action of the Cupressus sempervirens essential oil (CSEO) against Salmonella enterica Typhimuriumand Staphyloccocus aureus. The gas chromatography analysis revealed α-pinene (38.47%) and δ-3-carene (25.14%) are the major components of the CSEO. By using computational methods, such as quantitative structure-activity relationship (QSAR), we revealed that many CSEO components had no toxic effects. Moreover, findings indicated that α-pinene, δ-3-carene and borneol, a minor compound of CSEO, could inhibit the AcrB-TolC and MepR efflux pump activity of S. enterica Typhimurium and S. aureus, respectively. In addition, our molecular docking predictions indicated the high affinity of these three compounds with active sites of bacterial DNA and RNA polymerases, pointing to plausible impairments of the pathogenic bacteria cell replication processes. As well, the safety profile was developed through the zebrafish model. The in vivo toxicological evaluation of (CSEO) exhibited a concentration-dependent manner, with a lethal concentration (LC50) equal to 6.6 µg/mL.
Keywords: Cupressus sempervirens essential oil; antibacterial activity; computational toxicology; membrane permeability; molecular docking; replication and transcription inhibition; zebrafish.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures











Similar articles
-
In-Depth Study of Thymus vulgaris Essential Oil: Towards Understanding the Antibacterial Target Mechanism and Toxicological and Pharmacological Aspects.Biomed Res Int. 2022 Jul 21;2022:3368883. doi: 10.1155/2022/3368883. eCollection 2022. Biomed Res Int. 2022. PMID: 35909468 Free PMC article.
-
Unveiling the volatile compounds and antibacterial mechanisms of action of Cupressus sempervirens L., against Bacillus subtilis and Pseudomonas aeruginosa.Biomed Pharmacother. 2023 Nov;167:115609. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.115609. Epub 2023 Oct 4. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023. PMID: 37801906
-
The potency of Cupressus sempervirens and Eucalyptus globulus Essential Oils Against Antibiotic-Resistant Escherichia coli and Mammaliicoccus sciuri from Diseased Animals in Tunisia.Curr Microbiol. 2024 Nov 26;82(1):14. doi: 10.1007/s00284-024-03981-6. Curr Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39592457
-
Chemical composition, antimicrobial and antibiofilm activity of the essential oil and methanol extract of the Mediterranean cypress (Cupressus sempervirens L.).BMC Complement Altern Med. 2014 Jun 2;14:179. doi: 10.1186/1472-6882-14-179. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2014. PMID: 24890383 Free PMC article.
-
Activity and safety evaluation of natural preservatives.Food Res Int. 2024 Aug;190:114548. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2024.114548. Epub 2024 May 29. Food Res Int. 2024. PMID: 38945593 Review.
Cited by
-
In-Depth Study of Thymus vulgaris Essential Oil: Towards Understanding the Antibacterial Target Mechanism and Toxicological and Pharmacological Aspects.Biomed Res Int. 2022 Jul 21;2022:3368883. doi: 10.1155/2022/3368883. eCollection 2022. Biomed Res Int. 2022. PMID: 35909468 Free PMC article.
-
Antibacterial mechanism of action and in silico molecular docking studies of Cupressus funebris essential oil against drug resistant bacterial strains.Heliyon. 2023 Jul 27;9(8):e18742. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e18742. eCollection 2023 Aug. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37636470 Free PMC article.
-
Chemical Composition, In Vitro Antitumor Effect, and Toxicity in Zebrafish of the Essential Oil from Conyza bonariensis (L.) Cronquist (Asteraceae).Biomolecules. 2023 Sep 24;13(10):1439. doi: 10.3390/biom13101439. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 37892120 Free PMC article.
-
Disclosing the Functional Potency of Three Oxygenated Monoterpenes in Combating Microbial Pathogenesis: From Targeting Virulence Factors to Chicken Meat Preservation.Foods. 2024 Mar 21;13(6):965. doi: 10.3390/foods13060965. Foods. 2024. PMID: 38540955 Free PMC article.
-
Different essential oils can inhibit Candida albicans biofilm formation on acrylic resin by suppressing aspartic proteinase: In vitro and in silico approaches.Clin Oral Investig. 2025 Jan 28;29(2):94. doi: 10.1007/s00784-024-06039-w. Clin Oral Investig. 2025. PMID: 39875714
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

