A Strategy for Rapid Discovery of Marker Peptides Associated with Fibrinolytic Efficacy of Pheretima aspergillum Based on Bioinformatics Combined with Parallel Reaction Monitoring
- PMID: 35566002
- PMCID: PMC9100157
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27092651
A Strategy for Rapid Discovery of Marker Peptides Associated with Fibrinolytic Efficacy of Pheretima aspergillum Based on Bioinformatics Combined with Parallel Reaction Monitoring
Abstract
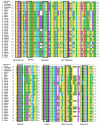
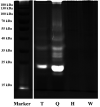
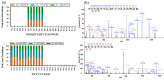
Quality control of animal-derived traditional Chinese medicines has improved dramatically as proteomics research advanced in the past few decades. However, it remains challenging to identify quality attributes with routine proteomics approaches since protein with fibrinolytic activity is rarely reported in pheretima, a typical animal-derived traditional medicine. A novel strategy based on bioinformatics combined with parallel reaction monitoring (PRM) was developed here to rapidly discover the marker peptides associated with a fibrinolytic effect. Potential marker peptides were found by lumbrokinase sequences' alignment and in silico digestion. The fibrinogen zymography was used to visually identify fibrinolytic proteins in pheretima. As a result, it was found that the fibrinolytic activity varied among different portions of pheretima. Fibrinolytic proteins were distributed regionally in the anterior and anterior-mid portion and there was no significant fibrinogenolytic activity observed in the mid-posterior and posterior portion. Finally, PRM experiments were deployed to validate and quantify selected marker peptides and a total of 11 peptides were identified as marker peptides, which could be potentially used in quality control of pheretima. This strategy provides a robust workflow to benefit the quality control of other animal-derived traditional medicines.
Keywords: Pheretima aspergillum; bioinformatics; fibrinolytic efficacy; lumbrokinase; parallel reaction monitoring.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Wang H.L., Li Q.L., Zhao H.P., Li C.Y. Research progress and strategy on identification and quality evaluation of animal-derived medicinal materials. Chin. Tradit. Herbal Drugs. 2018;48:3942–3949. doi: 10.7501/j.issn.0253-2670.2018.16.031. - DOI
-
- Lin C.Z., Li B.J., Han L.W. Analysis of projects funded by NSFC in field of Chinese materia medica quality evaluation in recent five years. Chin. Tradit. Herbal Drugs. 2020;51:281–286. doi: 10.7501/j.issn.0253-2670.2020.02.001. - DOI
-
- Yang H., Shen Y., Xu Y., Maqueda A.S., Zheng J., Wu Q., Tam J.P. A novel strategy for the discrimination of gelatinous Chinese medicines based on enzymatic digestion followed by nano-flow liquid chromatography in tandem with orbitrap mass spectrum detection. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015;10:4947–4955. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S82291. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cheng X.-L., Wei F., Xiao X.-Y., Zhao Y.-Y., Shi Y., Liu W., Zhang P., Ma S.-C., Tian S.-S., Lin R.-C. Identification of five gelatins by ultra performance liquid chromatography/time-of-flight mass spectrometry (UPLC/Q-TOF-MS) using principal component analysis. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2011;62:191–195. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2011.12.024. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

