G Protein-coupled Receptor (GPCR) Reconstitution and Labeling for Solution Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Studies of the Structural Basis of Transmembrane Signaling
- PMID: 35566006
- PMCID: PMC9101874
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27092658
G Protein-coupled Receptor (GPCR) Reconstitution and Labeling for Solution Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Studies of the Structural Basis of Transmembrane Signaling
Abstract
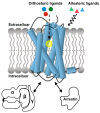
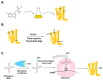
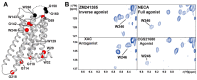
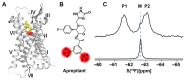
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) are a large membrane protein family found in higher organisms, including the human body. GPCRs mediate cellular responses to diverse extracellular stimuli and thus control key physiological functions, which makes them important targets for drug design. Signaling by GPCRs is related to the structure and dynamics of these proteins, which are modulated by extrinsic ligands as well as by intracellular binding partners such as G proteins and arrestins. Here, we review some basics of using nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy in solution for the characterization of GPCR conformations and intermolecular interactions that relate to transmembrane signaling.
Keywords: 19F-NMR; G protein-coupled receptors; amino-acid-specific NMR labeling; in-membrane chemical modification; membrane mimetics; sequence-specific NMR labeling; stable-isotope labeling.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

