Is There a Novel Biosynthetic Pathway in Mice That Converts Alcohol to Dopamine, Norepinephrine and Epinephrine?
- PMID: 35566075
- PMCID: PMC9105937
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27092726
Is There a Novel Biosynthetic Pathway in Mice That Converts Alcohol to Dopamine, Norepinephrine and Epinephrine?
Abstract
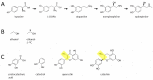
Previous studies in animals and humans have shown multiple types of interaction between alcohol (ethanol) intake and the catecholamine signaling molecules: dopamine, norepinephrine and epinephrine. This literature suggests that the administration of alcohol to rodents affects the central and peripheral (blood plasma) levels of these catecholamines. Two prior publications (Fitzgerald 2012, 2020) put forth the hypothesis that there may be a currently unidentified biosynthetic pathway, in a range of organisms, that actually converts alcohol to dopamine, norepinephrine and epinephrine. This publication describes the details for how to test this hypothesis in mice. Mice can be systemically injected with an intoxicating dose of commercially available stable isotope-labeled ethanol (ethanol-1-13C), and blood plasma samples and brains can be collected approximately two to 24 h post-injection. Liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry analysis can then be used to test whether some of the labeled ethanol molecules have been incorporated into new dopamine, norepinephrine, and epinephrine molecules, in plasma and brain samples. If confirmed, this hypothesis may have broadly reaching implications both for basic neuroscience and our understanding of alcohol abuse and alcoholism.
Keywords: addiction; catecholamines; dependence; ethanol; reward; substance abuse.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Investigating whether alcohol is transformed to norepinephrine or dopamine in the mouse brain.Pharmacol Rep. 2025 Jun;77(3):703-715. doi: 10.1007/s43440-025-00708-7. Epub 2025 Mar 12. Pharmacol Rep. 2025. PMID: 40069538
-
Many Drugs of Abuse May Be Acutely Transformed to Dopamine, Norepinephrine and Epinephrine In Vivo.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Oct 2;22(19):10706. doi: 10.3390/ijms221910706. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34639047 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neurodining: Common dietary factors may be substrates in novel biosynthetic pathways for monoaminergic neurotransmitters.Med Hypotheses. 2020 May;138:109618. doi: 10.1016/j.mehy.2020.109618. Epub 2020 Feb 11. Med Hypotheses. 2020. PMID: 32070787
-
A microdialysis profile of beta-endorphin and catecholamines in the rat nucleus accumbens following alcohol administration.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2003 Aug;169(1):60-7. doi: 10.1007/s00213-003-1490-2. Epub 2003 May 21. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2003. PMID: 12759807
-
How to prevent alcoholic liver disease.Exp Mol Pathol. 2015 Apr;98(2):304-7. doi: 10.1016/j.yexmp.2015.03.007. Epub 2015 Mar 7. Exp Mol Pathol. 2015. PMID: 25758202 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Several endocannabinoids and amino acids may be biosynthetically converted to catecholamines in vivo.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Jul 18;16:1614460. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1614460. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40756988 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Ethanol-Induced Depression: Exploring the Underlying Molecular Mechanisms.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2025 May 22;45(1):49. doi: 10.1007/s10571-025-01569-7. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2025. PMID: 40405002 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Investigating whether alcohol is transformed to norepinephrine or dopamine in the mouse brain.Pharmacol Rep. 2025 Jun;77(3):703-715. doi: 10.1007/s43440-025-00708-7. Epub 2025 Mar 12. Pharmacol Rep. 2025. PMID: 40069538
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

