Cytotoxicity Effect of Constituents of Pinus taiwanensis Hayata Twigs on B16-F10 Melanoma Cells
- PMID: 35566081
- PMCID: PMC9103300
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27092731
Cytotoxicity Effect of Constituents of Pinus taiwanensis Hayata Twigs on B16-F10 Melanoma Cells
Abstract
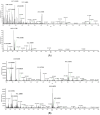
Pinus taiwanensis Hayata (Pinaceae) is an endemic plant in Taiwan. According to the Chinese Materia Medica Grand Dictionary, the Pinus species is mainly used to relieve pain, and eliminate pus and toxicity. In this study, nineteen compounds were isolated from the ethyl acetate layer of the ethanolic extract of P. taiwanensis Hayata twigs using bioassay-guided fractionation, and their anti-melanoma effects were investigated through a B16-F10 mouse melanoma cell model. The structures of the purified compounds were identified by 2D-NMR, MS, and IR, including 1 triterpenoid, 9 diterpenoids, 2 lignans, 4 phenolics, 1 phenylpropanoid, 1 flavonoid, and 1 steroid. Among them, compound 3 was found to be a new diterpene. Some of the compounds (2, 5, 6, 17, 18) showed moderate cytotoxicity effects. On the other hand, the anti-melanoma effect was no better than that from the original ethyl acetate layer. We presumed it resulted from the synergistic effect, although further experimentation needs to be performed.
Keywords: B16-F10 melanoma cells; Pinaceae; Pinus taiwanensis Hayata; UHPLC-MS/MS.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures





References
-
- National Cancer Institute. [(accessed on 12 November 2005)]; Available online: https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/melan.html.
-
- Murph M. Melanoma-Current Clinical Management and Future Therapeutics. University of Georgia; Athens, GA, USA: 2015.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

