Gene Interaction Network Analysis Reveals IFI44L as a Drug Target in Rheumatoid Arthritis and Periodontitis
- PMID: 35566100
- PMCID: PMC9104995
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27092749
Gene Interaction Network Analysis Reveals IFI44L as a Drug Target in Rheumatoid Arthritis and Periodontitis
Abstract
Objective: Despite extensive research on periodontitis and rheumatoid arthritis, the underlying molecular connectivity between these condition remains largely unknown. This research aimed to integrate periodontitis and rheumatoid arthritis gene expression profiles to identify interconnecting genes and focus to develop a common lead molecule against these inflammatory conditions.
Materials and methods: Differentially expressed genes (DEGs) of periodontitis and rheumatoid arthritis were identified from the datasets retrieved from the Gene Expression Omnibus database. The network was constructed by merging DEGs, and the interconnecting genes were identified and ranked using GeneMANIA. For the selected top ranked gene, the potential inhibitor was searched using FINDSITEcomb2.0. Subsequently, the molecular docking and molecular dynamics were performed to determine the binding efficiency and protein-ligand complex stability, respectively.
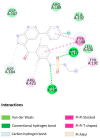
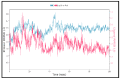
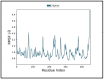
Results: From the network analysis, IFN-induced protein 44-like (IFI44L) was identified as a top ranked gene involved in most of the immunological pathway. With further virtual screening of 6507 molecules, vemurafenib was identified to be the best fit against the IFI44L target. The binding energy and stability of IFI44L with vemurafenib were investigated using molecular docking and molecular dynamics simulation. Docking results show binding energy of -7.7 Kcal/mol, and the simulation results show stability till 100 ns.
Conclusions: The identified IFI44L may represent a common drug target for periodontitis and rheumatoid arthritis. Vemurafenib could be a potent anti-inflammatory drug for both diseases.
Keywords: drug target; molecular docking; periodontitis; rheumatoid arthritis; vemurafenib.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Brief literature review and comprehensive bioinformatics analytics unravel the potential mechanism of curcumin in the treatment of periodontitis.BMC Oral Health. 2023 Jul 8;23(1):469. doi: 10.1186/s12903-023-03181-x. BMC Oral Health. 2023. Retraction in: BMC Oral Health. 2025 Mar 15;25(1):392. doi: 10.1186/s12903-025-05744-6. PMID: 37422651 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Integrated single-cell and bulk RNA sequencing identifies POSTN as a potential biomarker and therapeutic target for rheumatoid arthritis.Gene. 2024 Nov 30;928:148798. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2024.148798. Epub 2024 Jul 25. Gene. 2024. PMID: 39067546
-
The role of cellular senescence in the pathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis: Focus on IL-6 as a target gene.Cytokine. 2024 Dec;184:156762. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2024.156762. Epub 2024 Sep 25. Cytokine. 2024. PMID: 39326197
-
Immunological landscape of periodontitis and rheumatoid arthritis and their molecular crosstalk.Eur J Med Res. 2025 Feb 22;30(1):124. doi: 10.1186/s40001-025-02376-y. Eur J Med Res. 2025. PMID: 39987090 Free PMC article.
-
Bioinformatics Analysis and Identification of Genes and Molecular Pathways Involved in Synovial Inflammation in Rheumatoid Arthritis.Med Sci Monit. 2019 Mar 27;25:2246-2256. doi: 10.12659/MSM.915451. Med Sci Monit. 2019. PMID: 30916045 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Biomolecular and Biochemical Aspects of the Oral Cavity.Molecules. 2022 Dec 8;27(24):8676. doi: 10.3390/molecules27248676. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36557808 Free PMC article.
-
Unraveling IFI44L's biofunction in human disease.Front Oncol. 2024 Dec 16;14:1436576. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1436576. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39737399 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring animal models in oral cancer research and clinical intervention: A critical review.Vet Med Sci. 2023 Jul;9(4):1833-1847. doi: 10.1002/vms3.1161. Epub 2023 May 17. Vet Med Sci. 2023. PMID: 37196179 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extra Tree Classifier Predicts an Interactome Hub Gene as HSPB1 in Oral Cancer: A Bioinformatics Analysis.Cureus. 2024 May 8;16(5):e59863. doi: 10.7759/cureus.59863. eCollection 2024 May. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38854307 Free PMC article.
-
A Porphyromonas gingivalis hypothetical protein controlled by the type I-C CRISPR-Cas system is a novel adhesin important in virulence.mSystems. 2024 Mar 19;9(3):e0123123. doi: 10.1128/msystems.01231-23. Epub 2024 Feb 7. mSystems. 2024. PMID: 38323815 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hart T.C. Genetic considerations of risk in human periodontal disease. Curr. Opin. Periodontol. 1994;1994:3–11. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

