Characterization of Natural Anthocyanin Indicator Based on Cellulose Bio-Composite Film for Monitoring the Freshness of Chicken Tenderloin
- PMID: 35566103
- PMCID: PMC9103511
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27092752
Characterization of Natural Anthocyanin Indicator Based on Cellulose Bio-Composite Film for Monitoring the Freshness of Chicken Tenderloin
Abstract
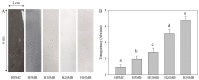
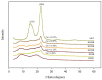
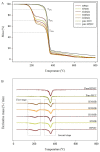
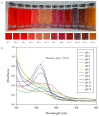
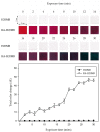
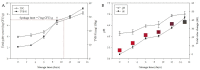
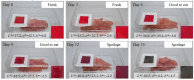
Intelligent packaging with indicators that provide information about the quality of food products can inform the consumer regarding food safety and reduce food waste. A solid material for a pH-responsive indicator was developed from hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC) composited with microcrystalline cellulose (MCC). MCC at 5%, 10%, 20%, and 30% w/w was introduced into the HPMC matrix and the physical, barrier, thermal, and optical properties of the HPMC/MCC bio-composite (HMB) films were analyzed. At 5, 10, and 20% MCC, improved mechanical, transparency, and barrier properties were observed, where HMB with 20% of MCC (H20MB) showed the best performance. Therefore, H20MB was selected as the biodegradable solid material for fabricating Roselle anthocyanins (RA) pH sensing indicators. The performance of the RA-H20MB indicator was evaluated by monitoring its response to ammonia vapor and tracking freshness status of chicken tenderloin. The RA-H20MB showed a clear color change with respect to ammonia exposure and quality change of chicken tenderloin; the color changed from red to magenta, purple and green, respectively. These results indicated that RA-H20MB can be used as a biodegradable pH sensing indicator to determine food quality and freshness.
Keywords: anthocyanin; bio-composite film; chicken tenderloin; hydroxypropyl methylcellulose; microcrystalline cellulose; pH sensing indicator.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Immobilization of roselle anthocyanins into polyvinyl alcohol/hydroxypropyl methylcellulose film matrix: Study on the interaction behavior and mechanism for better shrimp freshness monitoring.Int J Biol Macromol. 2021 Aug 1;184:666-677. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.06.074. Epub 2021 Jun 16. Int J Biol Macromol. 2021. PMID: 34146561
-
pH-responsive color indicator films based on methylcellulose/chitosan nanofiber and barberry anthocyanins for real-time monitoring of meat freshness.Int J Biol Macromol. 2021 Jan 1;166:741-750. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.10.231. Epub 2020 Oct 31. Int J Biol Macromol. 2021. PMID: 33137387
-
Functional characteristics improvement by structural modification of hydroxypropyl methylcellulose modified polyvinyl alcohol films incorporating roselle anthocyanins for shrimp freshness monitoring.Int J Biol Macromol. 2020 Nov 1;162:1250-1261. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.06.156. Epub 2020 Jun 20. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020. PMID: 32569695
-
Anthocyanin food colorant and its application in pH-responsive color change indicator films.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2021;61(14):2297-2325. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2020.1776211. Epub 2020 Jun 16. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2021. PMID: 32543217 Review.
-
Recent advances in pH-sensitive indicator films based on natural colorants for smart monitoring of food freshness: a review.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2024;64(33):12800-12819. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2023.2257327. Epub 2023 Sep 13. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2024. PMID: 37702748 Review.
Cited by
-
Recent Advances in Bio-Based Smart Active Packaging Materials.Foods. 2022 Jul 26;11(15):2228. doi: 10.3390/foods11152228. Foods. 2022. PMID: 35892814 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Preparation and Characterization of Theophylline Controlled Release Matrix System Incorporating Poloxamer 407, Stearyl Alcohol, and Hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose: A Novel Formulation and Development Study.Polymers (Basel). 2024 Feb 27;16(5):643. doi: 10.3390/polym16050643. Polymers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38475326 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Hydration Forms and Polymer Grades on Theophylline Controlled-Release Tablet: An Assessment and Evaluation.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Feb 21;17(3):271. doi: 10.3390/ph17030271. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38543057 Free PMC article.
-
Thermal and Sliding Wear Properties of Wood Waste-Filled Poly(Lactic Acid) Biocomposites.Polymers (Basel). 2022 May 30;14(11):2230. doi: 10.3390/polym14112230. Polymers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35683903 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanical Properties and Diffusion Studies in Wax-Cellulose Nanocomposite Packaging Material.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Aug 22;23(16):9501. doi: 10.3390/ijms23169501. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36012758 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ghaani M., Cozzolino C.A., Castelli G., Farris S. An overview of the intelligent packaging technologies in the food sector. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2016;51:1–11. doi: 10.1016/j.tifs.2016.02.008. - DOI
-
- Alizadeh-Sani M., Tavassoli M., Mohammadian E., Ehsani A., Khaniki G.J., Priyadarshi R., Rhim J.-W. pH-responsive color indicator films based on methylcellulose/chitosan nanofiber and barberry anthocyanins for real-time monitoring of meat freshness. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021;166:741–750. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.10.231. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

