Inverse Boltzmann Iterative Multi-Scale Molecular Dynamics Study between Carbon Nanotubes and Amino Acids
- PMID: 35566140
- PMCID: PMC9104776
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27092785
Inverse Boltzmann Iterative Multi-Scale Molecular Dynamics Study between Carbon Nanotubes and Amino Acids
Abstract
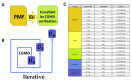
Our work uses Iterative Boltzmann Inversion (IBI) to study the coarse-grained interaction between 20 amino acids and the representative carbon nanotube CNT55L3. IBI is a multi-scale simulation method that has attracted the attention of many researchers in recent years. It can effectively modify the coarse-grained model derived from the Potential of Mean Force (PMF). IBI is based on the distribution result obtained by All-Atom molecular dynamics simulation; that is, the target distribution function and the PMF potential energy are extracted, and then, the initial potential energy extracted by the PMF is used to perform simulation iterations using IBI. Our research results have been through more than 100 iterations, and finally, the distribution obtained by coarse-grained molecular simulation (CGMD) can effectively overlap with the results of all-atom molecular dynamics simulation (AAMD). In addition, our work lays the foundation for the study of force fields for the simulation of the coarse-graining of super-large proteins and other important nanoparticles.
Keywords: CBNs; IBI; multi-scale molecular dynamics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
A coarse-grained model for polyethylene glycol polymer.J Chem Phys. 2011 Dec 7;135(21):214903. doi: 10.1063/1.3664623. J Chem Phys. 2011. PMID: 22149813
-
Molecular Dynamics Study of the Curvature-Driven Interactions between Carbon-Based Nanoparticles and Amino Acids.Molecules. 2023 Jan 4;28(2):482. doi: 10.3390/molecules28020482. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 36677540 Free PMC article.
-
C-IBI: Targeting cumulative coordination within an iterative protocol to derive coarse-grained models of (multi-component) complex fluids.J Chem Phys. 2016 May 7;144(17):174106. doi: 10.1063/1.4947253. J Chem Phys. 2016. PMID: 27155624
-
Coarse-graining methods for computational biology.Annu Rev Biophys. 2013;42:73-93. doi: 10.1146/annurev-biophys-083012-130348. Epub 2013 Feb 28. Annu Rev Biophys. 2013. PMID: 23451897 Review.
-
Systematic coarse-graining of the dynamics of entangled polymer melts: the road from chemistry to rheology.J Phys Condens Matter. 2011 Jun 15;23(23):233101. doi: 10.1088/0953-8984/23/23/233101. Epub 2011 May 25. J Phys Condens Matter. 2011. PMID: 21613700 Review.
References
-
- Arash B., Park H.S., Rabczuk T. Mechanical properties of carbon nanotube reinforced polymer nanocomposites: A coarse-grained model. Compos. Part B Eng. 2015;80:92–100. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2015.05.038. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

