Chemical Characteristics of Ethanol and Water Extracts of Black Alder (Alnus glutinosa L.) Acorns and Their Antibacterial, Anti-Fungal and Antitumor Properties
- PMID: 35566154
- PMCID: PMC9105167
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27092804
Chemical Characteristics of Ethanol and Water Extracts of Black Alder (Alnus glutinosa L.) Acorns and Their Antibacterial, Anti-Fungal and Antitumor Properties
Abstract
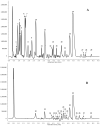
The aim of this study was to identify polyphenolic compounds contained in ethanol and water extracts of black alder (Alnus glutinosa L.) acorns and evaluate their anti-cancer and antimicrobial effects. The significant anti-cancer potential on the human skin epidermoid carcinoma cell line A431 and the human epithelial cell line A549 derived from lung carcinoma tissue was observed. Aqueous and ethanolic extracts of alder acorns inhibited the growth of mainly Gram-positive microorganisms (Staphylococcus aureus, Bacillus subtilis, Streptococcus mutans) and yeast-like fungi (Candida albicans, Candida glabrata), as well as Gram-negative (Escherichia coli, Citrobacter freundii, Proteus mirabilis, Pseudomonas aeruginosa) strains. The identification of polyphenols was carried out using an ACQUITY UPLC-PDA-MS system. The extracts were composed of 29 compounds belonging to phenolic acids, flavonols, ellagitannins and ellagic acid derivatives. Ellagitannins were identified as the predominant phenolics in ethanol and aqueous extract (2171.90 and 1593.13 mg/100 g DM, respectively) The results may explain the use of A. glutinosa extracts in folk medicine.
Keywords: UPLC-MS; anti-cancer effect; biological properties; extraction; polyphenolic compounds.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Antimicrobial activity of some Alnus species.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2015 Dec;19(23):4671-4. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2015. PMID: 26698267
-
Total phenolic and flavonoid contents, antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of Alnus glutinosa (L.) Gaertn., Alnus incana (L.) Moench and Alnus viridis (Chaix) DC. extracts.Nat Prod Res. 2014;28(24):2317-20. doi: 10.1080/14786419.2014.931390. Epub 2014 Jun 27. Nat Prod Res. 2014. PMID: 24969264
-
Glutinoin, a novel antioxidative ellagitannin from Alnus glutinosa cones with glutinoic acid dilactone moiety.Nat Prod Res. 2012;26(19):1806-16. doi: 10.1080/14786419.2011.613387. Epub 2011 Oct 11. Nat Prod Res. 2012. PMID: 21988712
-
Quantification of polyphenols and evaluation of antimicrobial, analgesic and anti-inflammatory activities of aqueous and acetone-water extracts of Libidibia ferrea, Parapiptadenia rigida and Psidium guajava.J Ethnopharmacol. 2014 Oct 28;156:88-96. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2014.07.031. Epub 2014 Aug 12. J Ethnopharmacol. 2014. PMID: 25124277
-
Screening for polyphenols, antioxidant and antimicrobial activitiesof extracts from eleven Helianthemum taxa (Cistaceae) used in folk medicine in south-eastern Spain.J Ethnopharmacol. 2013 Jun 21;148(1):287-96. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2013.04.028. Epub 2013 Apr 21. J Ethnopharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23615124
Cited by
-
Elderflowers (Sambuci flos L.): A Potential Source of Health-Promoting Components.Foods. 2024 Aug 16;13(16):2560. doi: 10.3390/foods13162560. Foods. 2024. PMID: 39200487 Free PMC article.
-
Leveraging crude extracts from European tree bark to combat oxidative stress, enhance wound healing, and inhibit pathogenic bacterial growth.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 1;15(1):21340. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-06105-7. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40596045 Free PMC article.
-
The Good, the Bad, and the Useable Microbes within the Common Alder (Alnus glutinosa) Microbiome-Potential Bio-Agents to Combat Alder Dieback.Microorganisms. 2023 Aug 30;11(9):2187. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11092187. Microorganisms. 2023. PMID: 37764031 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Seasonal Variation in Plant Polyphenols and Related Bioactivities across Three Years in Ten Tree Species as Visualized by Mass Spectrometric Fingerprint Mapping.Molecules. 2023 Aug 16;28(16):6093. doi: 10.3390/molecules28166093. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37630346 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dahija S., Čakar J., Vidic D., Maksimović M., Parić A. Total phenolic and flavo-noid contents, antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of Alnus glutinosa (L.) Gaertn., Alnus incana (L.) Moench and Alnus viridis (Chaix) DC. extracts. Nat. Prod. Res. 2014;28:2317–2320. doi: 10.1080/14786419.2014.931390. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Abedini A., Chollot S., Angelis A., Borie N., Nuzillard J.M., Skaltsounis A.L., Reynaud R., Gangloff S.C., Renault J.H., Hubert J. Bioactivity-guided identification of antimicrobial metabolites in Alnus glutinosa bark and optimization of oregonin purification by Centrifugal Partition Chromatography. J. Chromatogr. B. 2016;1:1029–1030. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2016.07.021. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Adebooye O.C., Alashi A.M., Aluko R.E. A brief review on emerging trends in global polyphenol research. J. Food Biochem. 2018;42:e12519. doi: 10.1111/jfbc.12519. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases