Optimization of an Ultra-Sonication Extraction Method for Major Compounds Found in Mondia whitei Using Design of Experiment
- PMID: 35566186
- PMCID: PMC9099649
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27092836
Optimization of an Ultra-Sonication Extraction Method for Major Compounds Found in Mondia whitei Using Design of Experiment
Abstract
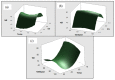
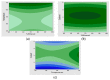
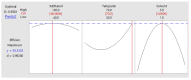
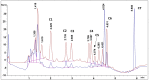
Optimum extraction conditions are vital in quality control methods to enable accurate quantification of the compounds of interest. An ultra-sonication method was developed for the extraction of seven major compounds found in Mondia whitei. Extraction temperature, time, power, frequency, percentage of ethanol in water and solvent to sample ratio were screened to access their significance on the percentage recovery of the compounds of interest. These parameters were screened using Descriptive screening design. Extraction temperature, solvent to sample ratio and the interaction between temperature and percentage ethanol in water were found to have a significant effect on the response. These parameters were then optimized using central composite design. The optimum conditions were found to be 66.1% ethanol in water, 70 °C temperature and 3 mL: 5 mg solvent to sample ratio. This method was successfully applied in the development of a quality control method for the seven compounds in Mondia whitei samples.
Keywords: Mondia whitei; central composite design; descriptive screening design; extraction; ultra-sonication.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Comparative antimalarial, toxicity and mito-protective effects of Diospyros mespiliformis Hochst. ex A. DC. and Mondia whitei (Hook.f.) Skeels on Plasmodium berghei infection in mice.J Ethnopharmacol. 2021 Mar 25;268:113585. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.113585. Epub 2020 Nov 12. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33189839
-
A Preliminary Evaluation of the Antibacterial Activity of Lemon Fruit Juice, Mondia whitei Ethanolic Extract, and Their Combination Against Streptococcus mutans.Infect Drug Resist. 2024 Oct 4;17:4291-4299. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S474810. eCollection 2024. Infect Drug Resist. 2024. PMID: 39381078 Free PMC article.
-
Establishment of ultrasound-assisted extraction of phenolic compounds from industrial potato by-products using response surface methodology.Food Chem. 2018 Dec 15;269:258-263. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.06.154. Epub 2018 Jul 2. Food Chem. 2018. PMID: 30100433
-
ISOLATION OF NOVEL PARA-PENTYL PHENYL BENZOATE FROM MONDIA WHITEI. (HOOK.F.) SKEELS (PERIPLOCACEAE), ITS STRUCTURE, SYNTHESIS AND NEUROPHARMACOLOGICAL EVALUATION.Afr J Tradit Complement Altern Med. 2016 Nov 23;14(1):219-230. doi: 10.21010/ajtcam.v14i1.24. eCollection 2017. Afr J Tradit Complement Altern Med. 2016. PMID: 28480400 Free PMC article.
-
Mondia whitei, a medicinal plant from Africa with aphrodisiac and antidepressant properties: a review.J Diet Suppl. 2012 Dec;9(4):272-84. doi: 10.3109/19390211.2012.726704. Epub 2012 Oct 8. J Diet Suppl. 2012. PMID: 23039023 Review.
References
-
- South African National Biodiversity. [(accessed on 4 December 2021)]. Available online: http://pza.sanbi.org/mondia-whitei.
-
- Aremu A.O., Cheesman L., Finnie J.F., Van Staden J. Mondia whitei (Apocynaceae): A review of its biological activities, conservation strategies and economic potential. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2011;77:960–971. doi: 10.1016/j.sajb.2011.06.010. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

