Isolation and HPLC Quantitative Determination of 5α-Reductase Inhibitors from Tectona grandis L.f. Leaf Extract
- PMID: 35566245
- PMCID: PMC9101728
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27092893
Isolation and HPLC Quantitative Determination of 5α-Reductase Inhibitors from Tectona grandis L.f. Leaf Extract
Abstract
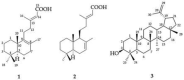
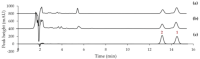
Steroid 5α-reductase plays a crucial role in catalyzing the conversion of testosterone to dihydrotestosterone, which is involved in many androgen-dependent disorders. Leaf-hexane extract from Tectona grandis L.f. has shown promise as a 5α-reductase inhibitor. The objectives of this current study were to isolate and identify 5α-reductase inhibitors from T. grandis leaves and to use them as the bioactive markers for standardization of the extract. Three terpenoid compounds, (+)-eperua-8,13-dien-15-oic acid (1), (+)-eperua-7,13-dien-15-oic acid (2), and lupeol (3), were isolated and evaluated for 5α-reductase inhibitory activity. Compounds 1 and 2 exhibited potent 5α-reductase inhibitory activity, while 3 showed weak inhibitory activity. An HPLC method for the quantitative determination of the two potent inhibitors (1 and 2), applicable for quality control of T. grandis leaf extracts, was also developed. The ethanolic extract showed a significantly higher content of 1 and 2 than found in the hexane extract, suggesting that ethanol is a preferable extraction solvent. This study is the first reported isolation of 5α-reductase inhibitors (1 and 2) from T. grandis leaves. The extraction and quality control methods that are safe and useful for further development of T. grandis leaf extract as an active ingredient for hair loss treatment products are also reported.
Keywords: 5α-reductase inhibitor; Tectona grandis; diterpenes; quality control.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Geographic Influence and Metabolomics-Driven Discovery of 5-Alpha Reductase Inhibitors in Tectona grandis L.f. (Teak) Leaves.Molecules. 2025 Jul 8;30(14):2895. doi: 10.3390/molecules30142895. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40733162 Free PMC article.
-
In Vitro Skin Penetration of 5α-Reductase Inhibitors from Tectona grandis L.f. Leaf Extracts.Molecules. 2025 Mar 4;30(5):1151. doi: 10.3390/molecules30051151. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40076375 Free PMC article.
-
Serenoa repens extracts: In vitro study of the 5α-reductase activity in a co-culture model for Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia.Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2018 Sep 30;90(3):199-202. doi: 10.4081/aiua.2018.3.199. Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2018. PMID: 30362688
-
Steroid 5alpha-reductase inhibitors.Mini Rev Med Chem. 2003 May;3(3):225-37. doi: 10.2174/1389557033488196. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2003. PMID: 12570838 Review.
-
Dihydrotestosterone and the concept of 5alpha-reductase inhibition in human benign prostatic hyperplasia.Eur Urol. 2000 Apr;37(4):367-80. doi: 10.1159/000020181. Eur Urol. 2000. PMID: 10765065 Review.
Cited by
-
Effectiveness and Safety of Hair Growth Formulation Containing Tectona grandis L.f (Teak) Leaf Extract: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study on Males with Androgenic Alopecia.J Evid Based Integr Med. 2024 Jan-Dec;29:2515690X241291141. doi: 10.1177/2515690X241291141. J Evid Based Integr Med. 2024. PMID: 39474646 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Geographic Influence and Metabolomics-Driven Discovery of 5-Alpha Reductase Inhibitors in Tectona grandis L.f. (Teak) Leaves.Molecules. 2025 Jul 8;30(14):2895. doi: 10.3390/molecules30142895. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40733162 Free PMC article.
-
In Vitro Skin Penetration of 5α-Reductase Inhibitors from Tectona grandis L.f. Leaf Extracts.Molecules. 2025 Mar 4;30(5):1151. doi: 10.3390/molecules30051151. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40076375 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources