Inhibitory Effects and Mechanism of the Natural Compound Diaporthein B Extracted from Marine-Derived Fungi on Colon Cancer Cells
- PMID: 35566295
- PMCID: PMC9101636
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27092944
Inhibitory Effects and Mechanism of the Natural Compound Diaporthein B Extracted from Marine-Derived Fungi on Colon Cancer Cells
Abstract
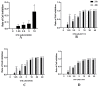
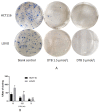
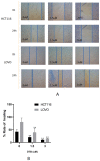
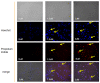
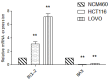
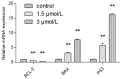
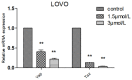
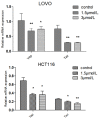
This study aimed to investigate the inhibitory effects and mechanism of diaporthein B (DTB), a natural compound extracted from the fungus Penicillium sclerotiorum GZU-XW03-2, on human colon cancer cells. The inhibitory effect of DTB at different concentrations on the proliferation of colon cancer cells HCT116 and LOVO was detected at 24 and 48 h. The effect of cell migration and clone formation ability were detected by cell scratch and plate cloning experiments. Morphological changes were observed by Hoechst 33342 and Annexin-V/PI staining, and flow cytometry was used to detect the proportion of apoptotic cells. DTB significantly inhibited colon cancer cell proliferation, migration, and apoptosis in a dose-dependent manner without significant effects on normal colonic epithelial cells NCM460. The IC50 inhibition effect can be achieved after treatment with 3 μmol/L DTB for 24 h. Compared with the blank group, the migration and clonal-forming ability of colon cancer cells in the DTB group was significantly decreased (p < 0.01), while the apoptotic cells were significantly increased (p < 0.01) in a concentration-dependent manner. DTB can inhibit the proliferation and migration of human colon cancer cells HCT116 and LOVO and promote the apoptosis of human colon cancer cells.
Keywords: DTB; Hippo; YAP; colon cancer; mitochondrial apoptosis pathway.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
[Inhibition effect of active fraction from clove on PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway to induce apoptosis of human colon cancer HCT116 cells].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2021 Mar;46(5):1197-1204. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20201027.401. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2021. PMID: 33787115 Chinese.
-
Screening of a composite library of clinically used drugs and well-characterized pharmacological compounds for cystathionine β-synthase inhibition identifies benserazide as a drug potentially suitable for repurposing for the experimental therapy of colon cancer.Pharmacol Res. 2016 Nov;113(Pt A):18-37. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2016.08.016. Epub 2016 Aug 10. Pharmacol Res. 2016. PMID: 27521834 Free PMC article.
-
Boswellic acid exerts potent anticancer effects in HCT-116 human colon cancer cells mediated via induction of apoptosis, cell cycle arrest, cell migration inhibition and inhibition of PI3K/AKT signalling pathway.J BUON. 2018 Mar-Apr;23(2):340-345. J BUON. 2018. PMID: 29745074
-
Gallic acid induced apoptotic events in HCT-15 colon cancer cells.World J Gastroenterol. 2016 Apr 21;22(15):3952-61. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i15.3952. World J Gastroenterol. 2016. PMID: 27099438 Free PMC article.
-
6-Shogaol Inhibits the Cell Migration of Colon Cancer by Suppressing the EMT Process Through the IKKβ/NF-κB/Snail Pathway.Integr Cancer Ther. 2023 Jan-Dec;22:15347354231172732. doi: 10.1177/15347354231172732. Integr Cancer Ther. 2023. PMID: 37157810 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The Cytotoxic Activity of Secondary Metabolites from Marine-Derived Penicillium spp.: A Review (2018-2024).Mar Drugs. 2025 Apr 30;23(5):197. doi: 10.3390/md23050197. Mar Drugs. 2025. PMID: 40422787 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bufalin targeting CAMKK2 inhibits the occurrence and development of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma through Wnt/β-catenin signal pathway.J Transl Med. 2023 Dec 11;21(1):900. doi: 10.1186/s12967-023-04613-6. J Transl Med. 2023. PMID: 38082327 Free PMC article.
-
A polyoxomolybdate-based hybrid nano capsule as an antineoplastic agent.Nanoscale Adv. 2023 Oct 6;5(22):6045-6052. doi: 10.1039/d3na00459g. eCollection 2023 Nov 7. Nanoscale Adv. 2023. PMID: 37941962 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ping X., Kuang H.X., Li X.L., Wang Y., Zhang B.M., Bu H., Wang Z.B., Meng Y.H., Wang Y.H., Wang Q.H. Proteomics and Its Application to Determine Mechanism of Action of Traditional Chinese Medicine. China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2018;43:904. - PubMed
-
- Ke Z., Chungeng L. Advances in the Basic Research of Traditional Chinese Medicine for the Treatment of Colon Cancer. Int. J. Trad. Chin. Med. 2020;42:936–938.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

