Multi-Element Analysis and Origin Discrimination of Panax notoginseng Based on Inductively Coupled Plasma Tandem Mass Spectrometry (ICP-MS/MS)
- PMID: 35566332
- PMCID: PMC9105934
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27092982
Multi-Element Analysis and Origin Discrimination of Panax notoginseng Based on Inductively Coupled Plasma Tandem Mass Spectrometry (ICP-MS/MS)
Abstract
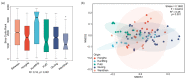
Panax notoginseng is an important functional health product, and has been used worldwide because of a wide range of pharmacological activities, of which the taproot is the main edible or medicinal part. However, the technologies for origin discrimination still need to be further studied. In this study, an ICP-MS/MS method for the accurate determination of 49 elements was established, whereby the instrumental detection limits (LODs) were between 0.0003 and 7.716 mg/kg, whereas the quantification limits (LOQs) were between 0.0011 and 25.7202 mg/kg, recovery of the method was in the range of 85.82% to 104.98%, and the relative standard deviations (RSDs) were lower than 10%. Based on the content of multi-element in P. notoginseng (total of 89 mixed samples), the discriminant models of origins and cultivation models were accurately determined by the neural networks (prediction accuracy was 0.9259 and area under ROC curve was 0.9750) and the support vector machine algorithm (both 1.0000), respectively. The discriminant models established in this study could be used to support transparency and traceability of supply chains of P. notoginseng and thus avoid the fraud of geographic identification.
Keywords: ICP-MS/MS; Panax notoginseng; cultivation model discrimination; multi-element; origin discrimination.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interest or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


References
-
- Yuan Z., Liao Y., Tian G., Li H., Jia Y., Zhang H., Tan Z., Li X., Deng W., Liu K., et al. Panax notoginseng saponins inhibit zymosan a induced atherosclerosis by suppressing integrin expression, FAK activation and NF-κB translocation. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2011;138:150–155. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2011.08.066. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Liao P., Liu P., Wang Y., Huang C., Lan L., Yang Y., Cui X. Stereoscopic cultivation of Panax notoginseng: A new approach to overcome the continuous cropping obstacle. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2018;126:38–47. doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2018.09.042. - DOI
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- 202102AE090042, 202102AA310048-2 and 2019ZG00901/Major Science and Technology Project of Yunnan and Kunming
- 2021JH002/Major Science and Technology Project of Kunming
- 202105AE160016/Innovative Research Team of Science and Technology in Yunnan Province
- 046180201 and 135305YJ01/Tianjin Normal University
- CARS-21/China Agriculture Research System
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

