The Role of the Nucleotides in the Insertion of the bis-Molybdopterin Guanine Dinucleotide Cofactor into apo-Molybdoenzymes
- PMID: 35566344
- PMCID: PMC9103625
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27092993
The Role of the Nucleotides in the Insertion of the bis-Molybdopterin Guanine Dinucleotide Cofactor into apo-Molybdoenzymes
Abstract
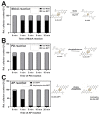
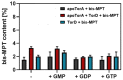
The role of the GMP nucleotides of the bis-molybdopterin guanine dinucleotide (bis-MGD) cofactor of the DMSO reductase family has long been a subject of discussion. The recent characterization of the bis-molybdopterin (bis-Mo-MPT) cofactor present in the E. coli YdhV protein, which differs from bis-MGD solely by the absence of the nucleotides, now enables studying the role of the nucleotides of bis-MGD and bis-MPT cofactors in Moco insertion and the activity of molybdoenzymes in direct comparison. Using the well-known E. coli TMAO reductase TorA as a model enzyme for cofactor insertion, we were able to show that the GMP nucleotides of bis-MGD are crucial for the insertion of the bis-MGD cofactor into apo-TorA.
Keywords: TMAO reductase; bis-MGD; chaperone; molybdenum cofactor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

