Construction of Enzyme-Responsive Micelles Based on Theranostic Zwitterionic Conjugated Bottlebrush Copolymers with Brush-on-Brush Architecture for Cell Imaging and Anticancer Drug Delivery
- PMID: 35566368
- PMCID: PMC9101325
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27093016
Construction of Enzyme-Responsive Micelles Based on Theranostic Zwitterionic Conjugated Bottlebrush Copolymers with Brush-on-Brush Architecture for Cell Imaging and Anticancer Drug Delivery
Abstract
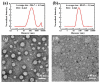
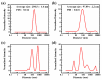
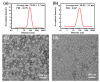
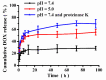
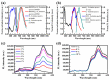
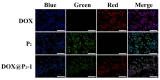
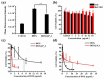
Bottlebrush copolymers with different chemical structures and compositions as well as diverse architectures represent an important kind of material for various applications, such as biomedical devices. To our knowledge, zwitterionic conjugated bottlebrush copolymers integrating fluorescence imaging and tumor microenvironment-specific responsiveness for efficient intracellular drug release have been rarely reported, likely because of the lack of an efficient synthetic approach. For this purpose, in this study, we reported the successful preparation of well-defined theranostic zwitterionic bottlebrush copolymers with unique brush-on-brush architecture. Specifically, the bottlebrush copolymers were composed of a fluorescent backbone of polyfluorene derivate (PFONPN) possessing the fluorescence resonance energy transfer with doxorubicin (DOX), primary brushes of poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate) (PHEMA), and secondary graft brushes of an enzyme-degradable polytyrosine (PTyr) block as well as a zwitterionic poly(oligo (ethylene glycol) monomethyl ether methacrylate-co-sulfobetaine methacrylate) (P(OEGMA-co-SBMA)) chain with super hydrophilicity and highly antifouling ability via elegant integration of Suzuki coupling, NCA ROP and ATRP techniques. Notably, the resulting bottlebrush copolymer, PFONPN9-g-(PHEMA15-g-(PTyr16-b-P(OEGMA6-co-SBMA6)2)) (P2) with a lower MW ratio of the hydrophobic side chains of PTyr and hydrophilic side chains of P(OEGMA-co-SBMA) could self-assemble into stabilized unimolecular micelles in an aqueous phase. The resulting unimolecular micelles showed a fluorescence quantum yield of 3.9% that is mainly affected by the pendant phenol groups of PTyr side chains and a drug-loading content (DLC) of approximately 15.4% and entrapment efficiency (EE) of 90.6% for DOX, higher than the other micelle analogs, because of the efficient supramolecular interactions of π-π stacking between the PTyr blocks and drug molecules, as well as the moderate hydrophilic chain length. The fluorescence of the PFONPN backbone enables fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) with DOX and visualization of intracellular trafficking of the theranostic micelles. Most importantly, the drug-loaded micelles showed accelerated drug release in the presence of proteinase K because of the enzyme-triggered degradation of PTyr blocks and subsequent deshielding of P(OEGMA-co-SBMA) corona for micelle destruction. Taken together, we developed an efficient approach for the synthesis of enzyme-responsive theranostic zwitterionic conjugated bottlebrush copolymers with a brush-on-brush architecture, and the resulting theranostic micelles with high DLC and tumor microenvironment-specific responsiveness represent a novel nanoplatform for simultaneous cell image and drug delivery.
Keywords: FRET; brush-on-brush; enzyme-responsive; theranostic; zwitterionic.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Synthesis of enzyme-responsive theranostic amphiphilic conjugated bottlebrush copolymers for enhanced anticancer drug delivery.Acta Biomater. 2022 May;144:15-31. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2022.03.028. Epub 2022 Mar 17. Acta Biomater. 2022. PMID: 35306183
-
Theranostic unimolecular micelles based on brush-shaped amphiphilic block copolymers for tumor-targeted drug delivery and positron emission tomography imaging.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2014 Dec 24;6(24):21769-79. doi: 10.1021/am5002585. Epub 2014 Mar 14. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2014. PMID: 24628452 Free PMC article.
-
Thermo-responsive drug release from self-assembled micelles of brush-like PLA/PEG analogues block copolymers.Int J Pharm. 2015 Aug 1;491(1-2):152-61. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2015.06.020. Epub 2015 Jun 18. Int J Pharm. 2015. PMID: 26095914
-
[Research progress on the fluorescence resonance energy transfer-based polymer micelles as drug carriers].Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 2022 Oct 25;39(5):1022-1032. doi: 10.7507/1001-5515.202111040. Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 2022. PMID: 36310492 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
-
Enhanced Optoelectronic Properties of Polythiophene-g-Poly(dimethyl amino ethyl methacrylate)-b-Poly(diethylene glycol methyl ether methacrylate) Copolymers using "Grafting onto" Synthetic Strategy.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2024 Sep 18;16(37):48854-48869. doi: 10.1021/acsami.4c13280. Epub 2024 Sep 4. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2024. PMID: 39231951 Review.
Cited by
-
Beyond Traditional Stimuli: Exploring Salt-Responsive Bottlebrush Polymers-Trends, Applications, and Perspectives.ACS Omega. 2024 Jul 26;9(31):33365-33385. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.4c06137. eCollection 2024 Aug 6. ACS Omega. 2024. PMID: 39130571 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Advances in Stimuli-Responsive Doxorubicin Delivery Systems for Liver Cancer Therapy.Polymers (Basel). 2022 Dec 1;14(23):5249. doi: 10.3390/polym14235249. Polymers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36501642 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current status, challenges and prospects of antifouling materials for oncology applications.Front Oncol. 2024 May 8;14:1391293. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1391293. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38779096 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Li Z., Tang M., Liang S., Zhang M., Biesold G.M., He Y., Hao S.-M., Choi W., Liu Y., Peng J., et al. Bottlebrush polymers: From controlled synthesis, self-assembly, properties to applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2021;116:101387. doi: 10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2021.101387. - DOI
-
- Guo J., Hong H., Chen G., Shi S., Nayak T.R., Theuer C.P., Barnhart T.E., Cai W., Gong S. Theranostic unimolecular micelles based on brush-shaped amphiphilic block copolymers for tumor-targeted drug delivery and positron emission tomography imaging. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 2014;6:21769–21779. doi: 10.1021/am5002585. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Jha S., Dutta S., Bowden N.B. Synthesis of Ultralarge Molecular Weight Bottlebrush Polymers Using Grubbs’ Catalysts. Macromolecules. 2004;37:4365–4374. doi: 10.1021/ma049647k. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

