Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids Provoke Apoptosis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma through Knocking Down the STAT3 Activated Signaling Pathway: In Vivo and In Vitro Study
- PMID: 35566382
- PMCID: PMC9103886
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27093032
Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids Provoke Apoptosis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma through Knocking Down the STAT3 Activated Signaling Pathway: In Vivo and In Vitro Study
Abstract
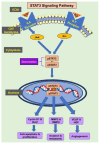
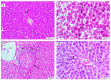
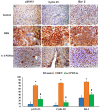
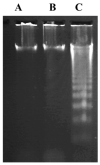
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a common type of liver cancer and is a leading cause of death worldwide. Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) is involved in HCC progression, migration, and suppression of apoptosis. This study investigates the apoptotic effect of the dietary antioxidant (n-3 PUFAs) on HepG2 cells and analyzes the underlying molecular mechanisms of this effect both in vivo and in vitro. In vivo study: Seventy-five adult male albino rats were divided into three groups (n = 25): Group I (control): 0.9% normal saline, intraperitoneal. Group II: N-Nitrosodiethylamine (200 mg/kg b.wt) intraperitoneal, followed by phenobarbital 0.05% in drinking water. Group III: as group II followed by n-3 PUFAs intubation (400 mg/kg/day). In vivo study: liver specimens for biochemical, histopathological, and immunohistochemical examination. In vitro study: MTT assay, cell morphology, PCR, Western blot, and immunohistochemical analysis. n-3 PUFAs significantly improved the histopathologic features of HCC and decreased the expression of anti-apoptotic proteins. Further, HepG2 cells proliferation was suppressed through inhibition of the STAT3 signaling pathway, cyclin D1, and Bcl-2 activity. Here we report that n-3 PUFAs may be an ideal cancer chemo-preventive candidate by targeting STAT3 signaling, which is involved in cell proliferation and apoptosis.
Keywords: Bcl-2; HepG2; STAT3; apoptosis; cyclin D1; n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Nitidine chloride inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma cell growth in vivo through the suppression of the JAK1/STAT3 signaling pathway.Int J Mol Med. 2013 Jul;32(1):79-84. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2013.1358. Epub 2013 Apr 22. Int J Mol Med. 2013. PMID: 23613111
-
Anticancer activity of dietary xanthone α-mangostin against hepatocellular carcinoma by inhibition of STAT3 signaling via stabilization of SHP1.Cell Death Dis. 2020 Jan 24;11(1):63. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-2227-4. Cell Death Dis. 2020. PMID: 31980595 Free PMC article.
-
Downregulation of protein disulfide‑isomerase A3 expression inhibits cell proliferation and induces apoptosis through STAT3 signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma.Int J Oncol. 2019 Apr;54(4):1409-1421. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2019.4710. Epub 2019 Feb 4. Int J Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30720090
-
Total alkaloids of Rubus aleaefolius Poir. inhibit the STAT3 signaling pathway leading to suppression of proliferation and cell cycle arrest in a mouse model of hepatocellular carcinoma.Oncol Rep. 2013 Sep;30(3):1309-14. doi: 10.3892/or.2013.2585. Epub 2013 Jul 3. Oncol Rep. 2013. PMID: 23828071
-
Potential role of signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT)3 signaling pathway in inflammation, survival, proliferation and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Jan;1835(1):46-60. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2012.10.002. Epub 2012 Oct 26. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 23103770 Review.
Cited by
-
Meeting at the Crossroad between Obesity and Hepatic Carcinogenesis: Unique Pathophysiological Pathways Raise Expectations for Innovative Therapeutic Approaches.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Sep 28;24(19):14704. doi: 10.3390/ijms241914704. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37834153 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Establishment and verification of a prognostic signature associated with fatty acid metabolism in endometrial cancer.Mol Med Rep. 2025 Mar;31(3):79. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2025.13444. Epub 2025 Jan 31. Mol Med Rep. 2025. PMID: 39886973 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

