A Novel Method for Digital Reconstruction of the Mucogingival Borderline in Optical Scans of Dental Plaster Casts
- PMID: 35566508
- PMCID: PMC9099921
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm11092383
A Novel Method for Digital Reconstruction of the Mucogingival Borderline in Optical Scans of Dental Plaster Casts
Abstract
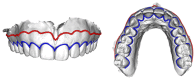
Adequate soft-tissue dimensions have been shown to be crucial for the long-term success of dental implants. To date, there is evidence that placement of dental implants should only be conducted in an area covered with attached gingiva. Modern implant planning software does not visualize soft-tissue dimensions. This study aims to calculate the course of the mucogingival borderline (MG-BL) using statistical shape models (SSM). Visualization of the MG-BL allows the practitioner to consider the soft tissue supply during implant planning. To deploy an SSM of the MG-BL, healthy individuals were examined and the intra-oral anatomy was captured using an intra-oral scanner (IOS). The empirical anatomical data was superimposed and analyzed by principal component analysis. Using a Leave-One-Out Cross Validation (LOOCV), the prediction of the SSM was compared with the original anatomy extracted from IOS. The median error for MG-BL reconstruction was 1.06 mm (0.49-2.15 mm) and 0.81 mm (0.38-1.54 mm) for the maxilla and mandible, respectively. While this method forgoes any technical work or additional patient examination, it represents an effective and digital method for the depiction of soft-tissue dimensions. To achieve clinical applicability, a higher number of datasets has to be implemented in the SSM.
Keywords: implant planning; mucogingival borderline; soft tissue dimensions; statistical shape model; virtual planning.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


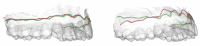
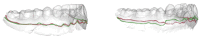
Similar articles
-
Creating an anatomical wax-up in partially edentulous patients by means of a statistical shape model.Int J Comput Dent. 2022 Nov 25;25(4):349-359. doi: 10.3290/j.ijcd.b2599407. Int J Comput Dent. 2022. PMID: 35072424
-
Accuracy of printed casts generated from digital implant impressions versus stone casts from conventional implant impressions: A comparative in vitro study.Clin Oral Implants Res. 2018 Aug;29(8):835-842. doi: 10.1111/clr.13297. Epub 2018 Jun 21. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2018. PMID: 29926977
-
Clinical and esthetic outcome with immediate insertion and provisionalization with or without connective tissue grafting in presence of mucogingival recessions: A retrospective analysis with follow-up between 1 and 8 years.Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2018 Jun;20(3):285-293. doi: 10.1111/cid.12595. Epub 2018 Mar 24. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2018. PMID: 29575589
-
Novel digital imaging techniques to assess the outcome in oral rehabilitation with dental implants: a narrative review.Clin Oral Implants Res. 2015 Sep;26 Suppl 11:86-96. doi: 10.1111/clr.12616. Epub 2015 May 26. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2015. PMID: 26010421 Review.
-
Soft tissue-related complications and management around dental implants.Periodontol 2000. 2019 Oct;81(1):124-138. doi: 10.1111/prd.12287. Periodontol 2000. 2019. PMID: 31407443 Review.
Cited by
-
Reconstruction of dental roots for implant planning purposes: a feasibility study.Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg. 2022 Oct;17(10):1957-1968. doi: 10.1007/s11548-022-02716-x. Epub 2022 Jul 29. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg. 2022. PMID: 35902422 Free PMC article.
-
Reconstruction of dental roots for implant planning purposes: a retrospective computational and radiographic assessment of single-implant cases.Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg. 2024 Mar;19(3):591-599. doi: 10.1007/s11548-023-02996-x. Epub 2023 Jul 31. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg. 2024. PMID: 37523011 Free PMC article.
-
Peri-implant phenotype, calprotectin and MMP-8 levels in cases diagnosed with peri-implant disease.Clin Oral Investig. 2024 Jun 28;28(7):404. doi: 10.1007/s00784-024-05798-w. Clin Oral Investig. 2024. PMID: 38940878 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brånemark P.I., Hansson B.O., Adell R., Breine U., Lindström J., Hallén O., Ohman A. Osseointegrated implants in the treatment of the edentulous jaw. Experience from a 10-year period. Scand. J. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. Suppl. 1977;16:10007349596. - PubMed
-
- Brånemark P.-I., Zarb G.A., Albrektsson T. Tissue-Integrated Prostheses: Osseointegration in Clinical Dentistry. Quintessence; Chicago, IL, USA: 1985.
-
- Saadoun A.P., LeGall M., Touati B. Selection and ideal tridimensional implant position for soft tissue aesthetics. Pract. Periodontics Aesthetic Dent. PPAD. 1999;11:1063–1072. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

