Postsurgical Thrombotic Microangiopathy and Deregulated Complement
- PMID: 35566627
- PMCID: PMC9100095
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm11092501
Postsurgical Thrombotic Microangiopathy and Deregulated Complement
Abstract
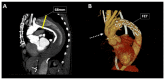
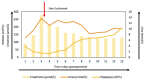
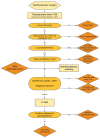
Postsurgical thrombotic microangiopathy (TMA) is a complication associated with significant morbidity and mortality. Still, the pathophysiological underlying mechanism of postsurgical TMA, a diagnosis often overlooked in postoperative patients with acute kidney injury and thrombocytopenia, is largely unknown. Here, we report the case of a 56-year-old male that developed anuric acute kidney injury, Coombs-negative hemolysis, and thrombocytopenia after surgical aortic arch replacement. Massive ex vivo complement activation on the endothelium, a rare complement gene variant in C2, at-risk haplotype MCPggaac, and excellent response to therapeutic complement inhibition, points to the pivotal role of complement in the pathophysiology of disease. Moreover, the importance of a multidisciplinary team approach in (postsurgical) thrombocytopenia is emphasized.
Keywords: aortic surgery; complement activation; complement inhibition; genetic variance; hemolytic uremic syndrome; multidisciplinary approach; thrombocytopenia; thrombotic micro-angiopathy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Kamla C.E., Grigorescu-Vlass M., Wassilowsky D., Fischereder M., Hagl C., Schönermarck U., Pichlmaier M.A., Peterss S., Jóskowiak D. Thrombotic microangiopathy following aortic surgery with hypothermic circulatory arrest: A single-centre experience of an underestimated cause of acute renal failure. Interact. Cardiovasc. Thorac. Surg. 2021;34:258–266. doi: 10.1093/icvts/ivab231. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sridharan M., Hook C.C., Leung N., Winters J.L., Go R.S. Mayo Clinic Complement Alternative Pathway-Thrombotic Microangiopathy Disease-Oriented Group Postsurgical Thrombotic Microangiopathy: Case Series and Review of the Literature. Eur. J. Haematol. 2019;103:307–318. doi: 10.1111/ejh.13284. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

