Analgesic and Functional Efficiency of High-Voltage Electrical Stimulation in Patients with Lateral Epicondylitis-A Report with a 180-Day Follow-Up
- PMID: 35566697
- PMCID: PMC9105087
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm11092571
Analgesic and Functional Efficiency of High-Voltage Electrical Stimulation in Patients with Lateral Epicondylitis-A Report with a 180-Day Follow-Up
Abstract
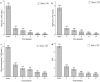
The available publications describing the beneficial effects of electrostimulation does not unequivocally confirm the clinical utility of high-voltage electrical stimulation (HVES) in the treatment of the lateral epicondylitis (LE). The aim of this study was the estimation of the effect of HVES on pain intensity and functional efficiency, both in the short and long term in patients with LE. The trial was registered by the Australian and New Zealand Clinical Trials Registry (ACTRN12621001389897). There were 58 patients allocated into two groups: the HVES group (n = 29, mean age 49.9 ± 11.0 years), treated with HVES (pulse duration: 200μs, frequency: 100 Hz, current amplitude in the range of 18-25 mA, voltage amplitude: 100 V), and the NORM group (n = 29, mean age 48.0 ± 12.6 years), who were healthy and untreated patients. The treatments were performed 5 days a week (from Monday to Friday) for two weeks. Treatment progress was measured by the visual analogue scale (VAS) for rest pain, night pain, and pain during activity; the Laitinen Pain Scale (LPS); and hand grip strength (HGS) before and after the treatment, as well as after 3, 6, 12, and 24 weeks. The reduction of pain (according to the VAS and LPS) and increase in the functional condition (according to the HGS) were observed in all HVES patients in the short- and long-term observation. Therefore, the HVES in treatment of LE was found to be effective and safe.
Keywords: hand grip strength; high-voltage electrical stimulation; lateral epicondylitis; pain intensity; tennis elbow; visual analogue scale.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Rodríguez-Huguet M., Góngora-Rodríguez J., Lomas-Vega R., Martín-Valero R., Díaz-Fernández Á., Obrero-Gaitán E., Ibáñez-Vera A.J., Rodríguez-Almagro D. Percutaneous Electrolysis in the Treatment of Lateral Epicondylalgia: A Single-Blind Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Clin. Med. 2020;9:2068. doi: 10.3390/jcm9072068. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Białek L., Franek A., Błaszczak E., Król T., Dolibog P., Białek J., Dolibog P., Wróbel B., Król P. Radial shockwave and ultrasound in the treatment of lateral epicondylitis—A preliminary report. Med. Rehabil. 2018;22:15–21. doi: 10.5604/01.3001.0012.0548. - DOI
-
- Ünver H.H., Bakılan F., Berkan Taşçıoğlu F., Armağan O., Özgen M. Comparing the efficacy of continuous and pulsed ultrasound therapies in patients with lateral epicondylitis: A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study. Turk. J. Phys. Med. Rehab. 2021;67:99–106. doi: 10.5606/tftrd.2021.4789. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

