Preoperative TAVR Planning: How to Do It
- PMID: 35566708
- PMCID: PMC9101424
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm11092582
Preoperative TAVR Planning: How to Do It
Abstract
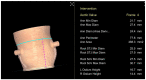
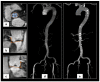
Transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) is a well-established treatment option for patients with severe symptomatic aortic stenosis (AS) whose procedural efficacy and safety have been continuously improving. Appropriate preprocedural planning, including aortic valve annulus measurements, transcatheter heart valve choice, and possible procedural complication anticipation is mandatory to a successful procedure. The gold standard for preoperative planning is still to perform a multi-detector computed angiotomography (MDCT), which provides all the information required. Nonetheless, 3D echocardiography and magnet resonance imaging (MRI) are great alternatives for some patients. In this article, we provide an updated comprehensive review, focusing on preoperative TAVR planning and the standard steps required to do it properly.
Keywords: 3D echocardiography; MDCT; MRI; TAVR; planning; sizing.
Conflict of interest statement
Tagliari A.P. had received a research grant from the Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior—Brasil (CAPES)—Finance Code 001. Saadi E.K. is a proctor in TAVI for Medtronic, Edwards and Abbott.
Figures
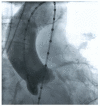
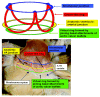
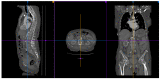
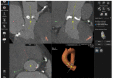

References
-
- Kapadia S.R., Leon M.B., Makkar R.R., Tuzcu E.M., Svensson L.G., Kodali S., Webb J.G., Mack M.J., Douglas P.S., Thourani V.H., et al. 5-year outcomes of transcatheter aortic valve replacement compared with standard treatment for patients with inoperable aortic stenosis (PARTNER 1): A randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2015;385:2485–2491. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(15)60290-2. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Mack M.J., Leon M.B., Thourani V.H., Makkar R., Kodali S.K., Russo M., Kapadia S.R., Malaisrie S.C., Cohen D.J., Pibarot P., et al. Transcatheter aortic-valve replacement with a balloon-expandable valve in low-risk patients. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019;380:1695–1705. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1814052. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Leon M.B., Smith C.R., Mack M., Miller D.C., Moses J.W., Svensson L.G., Tuzcu E.M., Webb J.G., Fontana G.P., Makkar R.R., et al. Transcatheter Aortic-Valve Implantation for Aortic Stenosis in Patients Who Cannot Undergo Surgery. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016;363:1511–1520. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1008232. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

