Investigation of Isotoxic Dose Escalation and Plan Quality with TDABC Analysis on a 0.35 T MR-Linac (MRL) System in Ablative 5-Fraction Stereotactic Magnetic Resonance-Guided Radiation Therapy (MRgRT) for Primary Pancreatic Cancer
- PMID: 35566712
- PMCID: PMC9104241
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm11092584
Investigation of Isotoxic Dose Escalation and Plan Quality with TDABC Analysis on a 0.35 T MR-Linac (MRL) System in Ablative 5-Fraction Stereotactic Magnetic Resonance-Guided Radiation Therapy (MRgRT) for Primary Pancreatic Cancer
Abstract
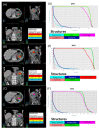
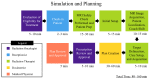
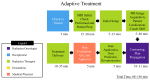
This study investigates plan quality generated by an MR-Linac (MRL) treatment planning system (TPS) for 5-fraction stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) of primary pancreatic cancer (PCa). In addition, an isotoxic dose escalation was investigated with the MRL TPS based on stereotactic MR-guided adaptive radiation therapy (SMART) trial constraints. A clinical workflow was developed for adaptive and non-adaptive treatments with the MRL, on which a time-driven activity-based costing (TDABC) analysis was performed to quantify clinical efficacy. Fifteen PCa patients previously treated with a conventional Linac were retrospectively re-planned for this study. Three plans were generated for each patient using the original prescription dose (PD) and organ at risk (OAR) constraints (Plan 1), following SMART trial's OAR constraints but with the original PD (Plan 2), starting with Plan 2, following an isotoxic dose escalation strategy where the dose was escalated until any one of the SMART trial's OAR constraints reached its limit (Plan 3). Conformity index (CI) and the ratio of the 50% isodose volume to PTV (R50%) conformity metrics were calculated for all 45 MRL plans, in addition to standard dose-volume indices. Forty-five MRL plans were created which met their respective dosimetric criteria described above. For Plan 1, the MRL TPS successfully achieved equivalent or lower OAR doses while maintaining the prescribed PTV coverage for the 15 plans. A maximum dose to the small bowel was reduced on average by 4.97 Gy (range: 1.11-10.58 Gy). For Plan 2, the MRL TPS successfully met all SMART trial OAR constraints while maintaining equivalent PTV coverage. For Plan 3, the MRL TPS was able to escalate the prescription dose from the original 25-33 Gy by, on average, 36 Gy (range: 15-70 Gy), and dose to the PTV was successfully escalated to at least 50 Gy for all 15 plans. These achievements were made possible, in part, due to the omission of the ITV afforded by the MRL's real-time target tracking technology and sharper dose penumbra due to its unique dual-focus MLC design. The 0.35T MRL TPS can generate plans that are equivalent to conventional Linac-based plans for SBRT of PCa. Through analyzing Plan 2 and 3 strategies, and due to the real-time target localization capabilities of the MRL system, increased OAR sparing and/or target dose escalation are possible.
Keywords: MR-Linac; MRgRT; dose escalation; pancreatic cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The impact of margin reduction on radiation dose distribution of ultra-hypofractionated prostate radiotherapy utilizing a 1.5-T MR-Linac.J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2024 Jan;25(1):e14179. doi: 10.1002/acm2.14179. Epub 2023 Nov 27. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2024. PMID: 38013636 Free PMC article.
-
Dosimetric comparison of MR-linac-based IMRT and conventional VMAT treatment plans for prostate cancer.Radiat Oncol. 2021 Jul 21;16(1):133. doi: 10.1186/s13014-021-01858-7. Radiat Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34289868 Free PMC article.
-
Dosimetric comparison of glioblastoma radiotherapy treatment plans on a low-field MRI-guided linear accelerator compared to conventional C-arm linear accelerator.Med Dosim. 2024 Autumn;49(3):215-221. doi: 10.1016/j.meddos.2023.12.004. Epub 2024 Jan 16. Med Dosim. 2024. PMID: 38233319
-
Stereotactic Magnetic Resonance-Guided Adaptive and Non-Adaptive Radiotherapy on Combination MR-Linear Accelerators: Current Practice and Future Directions.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Mar 30;15(7):2081. doi: 10.3390/cancers15072081. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37046741 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Treatment of Central Nervous System Tumors on Combination MR-Linear Accelerators: Review of Current Practice and Future Directions.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Oct 29;15(21):5200. doi: 10.3390/cancers15215200. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37958374 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Optimization of treatment workflow for 0.35T MR-Linac system.J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2024 Aug;25(8):e14393. doi: 10.1002/acm2.14393. Epub 2024 May 14. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2024. PMID: 38742819 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical experience with adaptive MRI-guided pancreatic SBRT and the use of abdominal compression to reduce treatment volume.Front Oncol. 2024 Aug 9;14:1441227. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1441227. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39184046 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of intrafraction motion in pancreatic cancer treatments with MR-guided adaptive radiation therapy.Front Oncol. 2023 Dec 13;13:1298099. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1298099. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 38162503 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical application of MR-Linac in tumor radiotherapy: a systematic review.Radiat Oncol. 2023 Mar 14;18(1):52. doi: 10.1186/s13014-023-02221-8. Radiat Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36918884 Free PMC article.
-
Does a peer review group consensus process for MR-Linac patients affect clinical care? Evaluation of impact and feasibility.Clin Transl Radiat Oncol. 2024 Jul 3;48:100816. doi: 10.1016/j.ctro.2024.100816. eCollection 2024 Sep. Clin Transl Radiat Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39130107 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Siegel Miller K.D., Fuchs H.E., Jemal A. Cancer Statistics. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021;71:7–33. - PubMed
-
- Tchelebi Lehrer E.J., Trifiletti D.M., Sharma N.K., Gusani N.J., Crane C.H., Zaorsky N.G. Conventionally fractionated radiation therapy versus stereotactic body radiation therapy for locally advanced pancreatic cancer (CRiSP): An international systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancer. 2020;126:2120–2131. doi: 10.1002/cncr.32756. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chuong Bryant J., Mittauer K.E., Hall M., Kotecha R., Alvarez D., Romaguera T., Rubens M., Adamson S., Godley A., Mishra V., et al. Ablative 5-Fraction Stereotactic Magnetic Resonance–Guided Radiation Therapy With On-Table Adaptive Replanning and Elective Nodal Irradiation for Inoperable Pancreas Cancer. Pract. Radiat. Oncol. 2021;11:134–147. doi: 10.1016/j.prro.2020.09.005. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Mahadevan Moningi S., Grimm J., Li X.A., Forster K.M., Palta M., Prior P., Goodman K.A., Narang A., Heron D.E., Lo S.S., et al. Maximizing Tumor Control and Limiting Complications With Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy for Pancreatic Cancer. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2021;110:206–216. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2020.11.017. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

