Disorders of the Calcium Sensing Signaling Pathway: From Familial Hypocalciuric Hypercalcemia (FHH) to Life Threatening Conditions in Infancy
- PMID: 35566721
- PMCID: PMC9100033
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm11092595
Disorders of the Calcium Sensing Signaling Pathway: From Familial Hypocalciuric Hypercalcemia (FHH) to Life Threatening Conditions in Infancy
Abstract
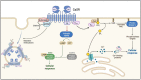
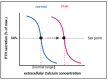
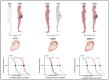
Familial hypocalciuric hypercalcemia (FHH) is a mostly benign condition of elevated calcium and PTH levels based on a hyposensitive calcium sensing receptor (CaSR) in FHH 1 or its downstream regulatory pathway in FHH2 and FHH3. In children, adolescents and young adults with FHH the main challenge is to distinguish the condition from primary hyperparathyroidism and thereby to avoid unnecessary treatments including parathyroidectomy. However, inheritance of FHH may result in neonatal hyperparathyroidism (NHPT) or neonatal severe hyperparathyroidism (NSHPT), conditions with high morbidity, and in the latter even high mortality. This review focuses on the genetic and pathophysiological framework that leads to the severe neonatal form, gives recommendations for counselling and summarizes treatment options.
Keywords: calcium sensing receptor (CaSR); cinacalcet; familial hypocalciuric hypercalcemia (FHH); neonatal hyperparathyroidism (NHPT); neonatal severe hyperparathyroidism (NSHPT).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Case Report: Severe Neonatal Course in Paternally Derived Familial Hypocalciuric Hypercalcemia.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021 Oct 1;12:700612. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.700612. eCollection 2021. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 34659108 Free PMC article.
-
Heterozygous inactivating CaSR mutations causing neonatal hyperparathyroidism: function, inheritance and phenotype.Eur J Endocrinol. 2016 Nov;175(5):421-31. doi: 10.1530/EJE-16-0223. Eur J Endocrinol. 2016. PMID: 27666534
-
Calcium signaling regulates trafficking of familial hypocalciuric hypercalcemia (FHH) mutants of the calcium sensing receptor.Mol Endocrinol. 2012 Dec;26(12):2081-91. doi: 10.1210/me.2012-1232. Epub 2012 Oct 17. Mol Endocrinol. 2012. PMID: 23077345 Free PMC article.
-
Cinacalcet therapy in a child with novel homozygous CASR p.Glu353Lys mutation causing familial hypocalciuric hypercalcemia type 1: case report and review of the literature.Turk J Pediatr. 2023;65(5):853-861. doi: 10.24953/turkjped.2022.1040. Turk J Pediatr. 2023. PMID: 37853976 Review.
-
GENETICS IN ENDOCRINOLOGY: Gain and loss of function mutations of the calcium-sensing receptor and associated proteins: current treatment concepts.Eur J Endocrinol. 2016 May;174(5):R189-208. doi: 10.1530/EJE-15-1028. Epub 2015 Dec 8. Eur J Endocrinol. 2016. PMID: 26646938 Review.
Cited by
-
The calcium-sensing receptor: a comprehensive review on its role in calcium homeostasis and therapeutic implications.Am J Transl Res. 2025 Mar 15;17(3):2322-2338. doi: 10.62347/QGTS5711. eCollection 2025. Am J Transl Res. 2025. PMID: 40226019 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pediatric Neuroendocrine Neoplasia of the Parathyroid Glands: Delving into Primary Hyperparathyroidism.Biomedicines. 2023 Oct 17;11(10):2810. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11102810. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37893182 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Familial hypocalciuric hypercalcaemia type 1 caused by a novel heterozygous missense variant in the CaSR gene, p(His41Arg): two case reports.BMC Endocr Disord. 2022 Dec 19;22(1):324. doi: 10.1186/s12902-022-01231-z. BMC Endocr Disord. 2022. PMID: 36536367 Free PMC article.
-
Retrospectively diagnosed familial hypocalciuric hypercalcaemia following total parathyroidectomy in an asymptomatic patient.EJIFCC. 2024 Dec 30;35(4):329-332. eCollection 2024 Dec. EJIFCC. 2024. PMID: 39810898 Free PMC article.
-
Case Report: Familial hypocalciuric hypercalcemia type 1 with a novel mutation combined with Gitelman syndrome and a review of the literature.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025 Feb 25;16:1503128. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1503128. eCollection 2025. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40070587 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

