Robotic Living Donor Right Hepatectomy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 35566727
- PMCID: PMC9103024
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm11092603
Robotic Living Donor Right Hepatectomy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
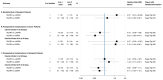
The introduction of robotics in living donor liver transplantation has been revolutionary. We aimed to examine the safety of robotic living donor right hepatectomy (RLDRH) compared to open (ODRH) and laparoscopic (LADRH) approaches. A systematic review was carried out in Medline and six additional databases following PRISMA guidelines. Data on morbidity, postoperative liver function, and pain in donors and recipients were extracted from studies comparing RLDRH, ODRH, and LADRH published up to September 2020; PROSPERO (CRD42020214313). Dichotomous variables were pooled as risk ratios and continuous variables as weighted mean differences. Four studies with a total of 517 patients were included. In living donors, the postoperative total bilirubin level (MD: −0.7 95%CI −1.0, −0.4), length of hospital stay (MD: −0.8 95%CI −1.4, −0.3), Clavien−Dindo complications I−II (RR: 0.5 95%CI 0.2, 0.9), and pain score at day > 3 (MD: −0.6 95%CI −1.6, 0.4) were lower following RLDRH compared to ODRH. Furthermore, the pain score at day > 3 (MD: −0.4 95%CI −0.8, −0.09) was lower after RLDRH when compared to LADRH. In recipients, the postoperative AST level was lower (MD: −0.5 95%CI −0.9, −0.1) following RLDRH compared to ODRH. Moreover, the length of stay (MD: −6.4 95%CI −11.3, −1.5) was lower after RLDRH when compared to LADRH. In summary, we identified low- to unclear-quality evidence that RLDRH seems to be safe and feasible for adult living donor liver transplantation compared to the conventional approaches. No postoperative deaths were reported.
Keywords: liver transplantation; meta-analysis; robot; systematic review.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

