Port Placement Strategies for Robotic Pulmonary Lobectomy: A Narrative Review
- PMID: 35566741
- PMCID: PMC9103382
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm11092612
Port Placement Strategies for Robotic Pulmonary Lobectomy: A Narrative Review
Abstract
Background: Despite the use of robotics becoming increasingly popular among thoracic surgeons worldwide, there remains debate over the best robotic approach for lung resections. In this paper, we delineated the main port placement strategies and discussed their advantages and disadvantages.
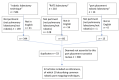
Methods: A PubMed literature review was performed using key phrases such as "robotic lobectomy technique", "RATS lobectomy", and "port placement robotic lobectomy". After the final review, 22 articles were included as references, of which 10 described common robotic port mapping techniques.
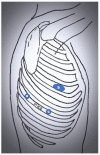
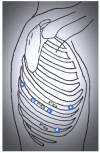
Results: Several port strategies for robot-assisted pulmonary lobectomies have been proposed and described in the literature, each showing its own limitations and advantages.
Conclusions: New robotic surgeons may choose their port strategy according to personal preference and previous surgical experience, especially regarding open or VATS resections. Robust data comparing different port placements in robotic surgery are lacking. Further research should be directed toward comparisons of clinical outcomes with different robotic approaches.
Keywords: RATS; port mapping; robotic approach; robotic lobectomy; robotic surgery; surgical technique.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

