OSDI Questions on Daily Life Activities Allow to Detect Subclinical Dry Eye in Young Contact Lens Users
- PMID: 35566752
- PMCID: PMC9101005
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm11092626
OSDI Questions on Daily Life Activities Allow to Detect Subclinical Dry Eye in Young Contact Lens Users
Abstract
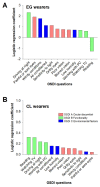
Dry eye disease (DED) is difficult to detect in young contact lens (CL) wearers, who usually have no signs, mild symptoms and an ocular surface disease index (OSDI) below the DED diagnosis values (OSDI ≥ 13). We investigate if some of the 12 OSDI questions (OSDI A—ocular symptoms; OSDI B—vision-related functionality; OSDI C—environmental triggers) contribute the most to classify young CL as symptomatic. TBUT and tear volume are also measured. Age, gender and refraction error-matched eye glasses (EG) wearers participated as the control. CL and EG data were compared with t-test and z-test. Confusion matrices and logistic correlation analyses were performed to define the contribution of each OSDI question to classify symptomatic subjects. OSDI classified symptomatic CL better than the tear volume or TBUT values. In CL, only OSDI B and C values were significantly higher in symptomatic vs. asymptomatic subjects (p < 0.001), while values of all twelve OSDI questions were significantly higher in symptomatic vs. asymptomatic EG (p < 0.05−0.001). All OSDI questions contribute equally to identify symptomatic EG, while only OSDI B questions on daily life visual functions are significant to classify symptomatic CL wearers at risk to develop DED or at a subclinical stage. CL wearers scoring ≥ 2 on the OSDI B questions should be considered for preventive treatments, even if their clinical sings are scarce or absent.
Keywords: OSDI; contact lens; daily life activities; dry eye disease symptoms; ocular symptoms evaluation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Abetz L., Rajagopalan K., Mertzanis P., Begley C., Barnes R., Chalmers R. Development and validation of the impact of dry eye on everyday life (IDEEL) questionnaire, a patient-reported outcomes (PRO) measure for the assessment of the burden of dry eye on patients. Health Qual. Life Outcomes. 2011;9:111. doi: 10.1186/1477-7525-9-111. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- McMonnies C.W., Ho A. Responses to a dry eye questionnaire from a normal population. J. Am. Optom. Assoc. 1987;58:588–591. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

