Marginal versus Standard Donors in Heart Transplantation: Proper Selection Means Heart Transplant Benefit
- PMID: 35566789
- PMCID: PMC9105473
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm11092665
Marginal versus Standard Donors in Heart Transplantation: Proper Selection Means Heart Transplant Benefit
Abstract
Background: In this study, we assessed the mid-term outcomes of patients who received a heart donation from a marginal donor (MD), and compared them with those who received an organ from a standard donor (SD).
Methods: All patients who underwent HTx between January 2012 and December 2020 were enrolled at a single institution. The primary endpoints were early and long-term survival of MD recipients. Risk factors for primary graft failure (PGF) and mortality in MD recipients were also analyzed. The secondary endpoint was the comparison of survival of MD versus SD recipients.
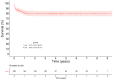
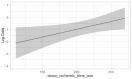
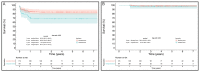
Results: In total, 238 patients underwent HTx, 64 (26.9%) of whom received an organ from an MD. Hospital mortality in the MD recipient cohort was 23%, with an estimated 1 and 5-year survival of 70% (59.2-82.7) and 68.1% (57.1-81), respectively. A multivariate analysis in MD recipients showed that decreased renal function and increased inotropic support of recipients were associated with higher mortality (p = 0.04 and p = 0.03). Cold ischemic time (p = 0.03) and increased donor inotropic support (p = 0.04) were independent risk factors for PGF. Overall survival was higher in SD than MD (85% vs. 68% at 5 years, log-rank = 0.008). However, risk-adjusted mortality (p = 0.2) and 5-year conditional survival (log-rank = 0.6) were comparable.
Conclusions: Selected MDs are a valuable resource for expanding the cardiac donor pool, showing promising results. The use of MDs after prolonged ischemic times, increased inotropic support of the MD or the recipient and decreased renal function are associated with worse outcomes.
Keywords: heart marginal donors; in-hospital mortality; mid-term survival; standard donors and marginal donors’ comparison.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Mehra M.R., Canter C.E., Hannan M.M., Semigran M.J., Uber P.A., Baran D.A., Danziger-Isakov L., Kirklin J.K., Kirk R., Kushwaha S.S., et al. International Society for Heart Lung Transplantation (ISHLT) Infectious Diseases, Pediatric and Heart Failure and Transplantation Councils. The 2016 International Society for Heart Lung Transplantation listing criteria for heart transplantation: A 10-year update. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2016;35:1–23. doi: 10.1016/j.healun.2015.10.023. - DOI - PubMed
-
- [(accessed on 21 August 2021)]; Available online: https://www.trapianti.salute.gov.it/imgs/C_17_cntPubblicazioni_415_alleg....
-
- Apostolo A., Paolillo S., Contini M., Vignati C., Tarzia V., Campodonico J., Mapelli M., Massetti M., Bejko J., Righini F., et al. Comprehensive effects of left ventricular assist device speed changes on alveolar gas exchange, sleep ventilatory pattern, and exercise performance. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2018;37:1361–1371. doi: 10.1016/j.healun.2018.07.005. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

