Applications of Polymers for Organ-on-Chip Technology in Urology
- PMID: 35566836
- PMCID: PMC9105302
- DOI: 10.3390/polym14091668
Applications of Polymers for Organ-on-Chip Technology in Urology
Abstract
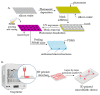
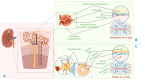
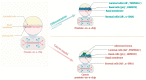
Organ-on-chips (OOCs) are microfluidic devices used for creating physiological organ biomimetic systems. OOC technology brings numerous advantages in the current landscape of preclinical models, capable of recapitulating the multicellular assemblage, tissue-tissue interaction, and replicating numerous human pathologies. Moreover, in cancer research, OOCs emulate the 3D hierarchical complexity of in vivo tumors and mimic the tumor microenvironment, being a practical cost-efficient solution for tumor-growth investigation and anticancer drug screening. OOCs are compact and easy-to-use microphysiological functional units that recapitulate the native function and the mechanical strain that the cells experience in the human bodies, allowing the development of a wide range of applications such as disease modeling or even the development of diagnostic devices. In this context, the current work aims to review the scientific literature in the field of microfluidic devices designed for urology applications in terms of OOC fabrication (principles of manufacture and materials used), development of kidney-on-chip models for drug-toxicity screening and kidney tumors modeling, bladder-on-chip models for urinary tract infections and bladder cancer modeling and prostate-on-chip models for prostate cancer modeling.
Keywords: bladder-on-chip; kidney-on-chip; organ-on-chip; polymeric microfluidic devices; prostate-on-chip; tumor-on-chip.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Zanetti F. Organ-on-a-Chip. Elsevier; Amsterdam, The Netherlands: 2020. Kidney-on-a-Chip; pp. 233–253.
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

