A Highly Active Chondroitin Sulfate Lyase ABC for Enzymatic Depolymerization of Chondroitin Sulfate
- PMID: 35566938
- PMCID: PMC9100776
- DOI: 10.3390/polym14091770
A Highly Active Chondroitin Sulfate Lyase ABC for Enzymatic Depolymerization of Chondroitin Sulfate
Abstract
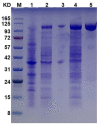
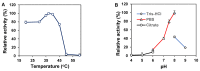
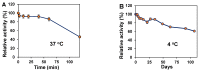
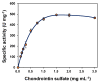
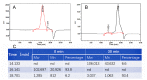
Enzymatic preparation of low-molecular-weight chondroitin sulfate (LMWCS) has received increasing attention. In this work, a chondroitin sulfate lyase ABC (Chon-ABC) was successfully cloned, expressed, and characterized. The Km and Vmax of the Chon-ABC were 0.54 mM and 541.3 U mg-1, respectively. The maximal activity was assayed as 500.4 U mg-1 at 37 °C in pH 8.0 phosphate buffer saline. The half-lives of the Chon-ABC were 133 d and 127 min at 4 °C and 37 °C, respectively. Enzymatic preparation of LMWCS was performed at room temperature for 30 min. The changes between the substrate and product were analyzed with mass spectrometry (MS), high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), gel permeation chromatography (GPC), and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR). Overall, the Chon-ABC from Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron is competitive in large-scale enzymatic preparation of LMWCS for its high activity, stability, and substrate specificity.
Keywords: Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron; characterization; depolymerization; high activity; low-molecular-weight chondroitin sulfate.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interest or personal relationship that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures




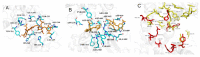
Similar articles
-
Purification and characterization of novel chondroitin ABC and AC lyases from Bacteroides stercoris HJ-15, a human intestinal anaerobic bacterium.Eur J Biochem. 2002 Jun;269(12):2934-40. doi: 10.1046/j.1432-1033.2002.02967.x. Eur J Biochem. 2002. PMID: 12071957
-
Characterization of chondroitin sulfate lyase ABC from Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron WAL2926.Biochemistry. 2008 Jun 24;47(25):6650-61. doi: 10.1021/bi800353g. Biochemistry. 2008. PMID: 18512954
-
A novel chondroitin AC lyase from Pedobacter xixiisoli: Cloning, expression, characterization and the application in the preparation of oligosaccharides.Enzyme Microb Technol. 2021 May;146:109765. doi: 10.1016/j.enzmictec.2021.109765. Epub 2021 Feb 19. Enzyme Microb Technol. 2021. PMID: 33812567
-
Effects of hyaluronan lyase, hyaluronidase, and chondroitin ABC lyase on mammalian vitreous gel.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1999 Sep;40(10):2173-8. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1999. PMID: 10476780
-
Structural variation of chondroitin sulfate and its roles in the central nervous system.Cent Nerv Syst Agents Med Chem. 2010 Mar;10(1):22-31. doi: 10.2174/187152410790780136. Cent Nerv Syst Agents Med Chem. 2010. PMID: 20236040 Review.
Cited by
-
Comparison of chemonucleolysis and discectomy in the management of lumbar disc herniation: a comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis.Neurosurg Rev. 2025 Apr 3;48(1):347. doi: 10.1007/s10143-025-03501-5. Neurosurg Rev. 2025. PMID: 40175852
-
Physically Crosslinked Chondroitin Sulfate (CS)-Metal Ion (M: Fe(III), Gd(III), Zn(II), and Cu(II)) Particles for Versatile Applications and Their Biosafety.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Mar 23;16(4):483. doi: 10.3390/ph16040483. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37111240 Free PMC article.
-
The efficacy and safety of condoliase for lumbar disc herniation: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Aug 21;14:1151998. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1151998. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37670940 Free PMC article.
References
-
- He M., Wang J., Hu S., Wang Y., Xue C., Li H. The Effects of Fucosylated Chondroitin Sulfate Isolated from Isostichopus Badionotus on Antimetastatic Activity via Down-Regulation of Hif-1α and Hpa. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2014;23:1643–1651. doi: 10.1007/s10068-014-0224-z. - DOI
-
- Li J., Li S., Yan L., Ding T., Linhardt R.J., Yu Y., Liu X., Liu D., Ye X., Chen S. Fucosylated Chondroitin Sulfate Oligosaccharides Exert Anticoagulant Activity by Targeting at Intrinsic Tenase Complex with Low FXII Activation: Importance of Sulfation Pattern and Molecular Size. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017;139:191–200. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2017.07.065. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

