Tailoring of Geranium Oil-Based Nanoemulsion Loaded with Pravastatin as a Nanoplatform for Wound Healing
- PMID: 35567079
- PMCID: PMC9105023
- DOI: 10.3390/polym14091912
Tailoring of Geranium Oil-Based Nanoemulsion Loaded with Pravastatin as a Nanoplatform for Wound Healing
Abstract
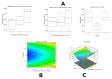
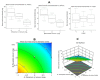
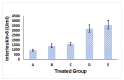
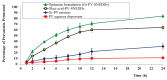
The healing of a burn wound is a complex process that includes the re-formation of injured tissues and the control of infection to minimize discomfort, scarring, and inconvenience. The current investigation's objective was to develop and optimize a geranium oil-based self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery system loaded with pravastatin (Gr-PV-NE). The geranium oil and pravastatin were both used due to their valuable anti-inflammatory and antibacterial activities. The Box-Behnken design was chosen for the development and optimization of the Gr-PV-NE. The fabricated formulations were assessed for their droplet size and their effects on the burn wound diameter in experimental animals. Further, the optimal formulation was examined for its wound healing properties, antimicrobial activities, and ex-vivo permeation characteristics. The produced nanoemulsion had a droplet size of 61 to 138 nm. The experimental design affirmed the important synergistic influence of the geranium oil and pravastatin for the healing of burn wounds; it showed enhanced wound closure and improved anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial actions. The optimal formulation led to a 4-fold decrease in the mean burn wound diameter, a 3.81-fold lowering of the interleukin-6 serum level compared to negative control, a 4-fold increase in the inhibition zone against Staphylococcus aureus compared to NE with Gr oil, and a 7.6-fold increase in the skin permeation of pravastatin compared to PV dispersion. Therefore, the devised nanoemulsions containing the combination of geranium oil and pravastatin could be considered a fruitful paradigm for the treatment of severe burn wounds.
Keywords: Box–Behnken design; burn wound; essential oil; ex-vivo permeation; nanotechnology; statins.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Coconut Oil Nanoemulsion Loaded with a Statin Hypolipidemic Drug for Management of Burns: Formulation and In Vivo Evaluation.Pharmaceutics. 2020 Nov 7;12(11):1061. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics12111061. Pharmaceutics. 2020. PMID: 33171816 Free PMC article.
-
Formulation and characterization of propolis and tea tree oil nanoemulsion loaded with clindamycin hydrochloride for wound healing: In-vitro and in-vivo wound healing assessment.Saudi Pharm J. 2021 Nov;29(11):1238-1249. doi: 10.1016/j.jsps.2021.10.004. Epub 2021 Oct 19. Saudi Pharm J. 2021. PMID: 34819785 Free PMC article.
-
Diosmin-Loaded Nanoemulsion-Based Gel Formulation: Development, Optimization, Wound Healing and Anti-Inflammatory Studies.Gels. 2023 Jan 22;9(2):95. doi: 10.3390/gels9020095. Gels. 2023. PMID: 36826265 Free PMC article.
-
Implementation of Quality by Design (QbD) approach in development of silver sulphadiazine loaded egg oil organogel: An improved dermatokinetic profile and therapeutic efficacy in burn wounds.Int J Pharm. 2020 Feb 25;576:118977. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2019.118977. Epub 2019 Dec 21. Int J Pharm. 2020. PMID: 31870953
-
Fabrication and Optimization of Essential-Oil-Loaded Nanoemulsion Using Box-Behnken Design against Staphylococos aureus and Staphylococos epidermidis Isolated from Oral Cavity.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Aug 5;14(8):1640. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14081640. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 36015266 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The Antibacterial and Wound Healing Properties of Natural Products: A Review on Plant Species with Therapeutic Potential against Staphylococcus aureus Wound Infections.Plants (Basel). 2023 May 29;12(11):2147. doi: 10.3390/plants12112147. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37299127 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pharmacodynamic Studies of Pravastatin Sodium Nanoemulsion Loaded Transdermal Patch for Treatment of Hyperlipidemia.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2024 Feb 8;25(2):34. doi: 10.1208/s12249-024-02746-5. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2024. PMID: 38332233
-
Essential Oils of Some Potential Medicinal Plants and their Wound Healing Activities.Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2024;25(14):1818-1834. doi: 10.2174/0113892010282605231218064053. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38310452 Review.
-
Polymer Materials for Drug Delivery and Tissue Engineering.Polymers (Basel). 2023 Jul 21;15(14):3103. doi: 10.3390/polym15143103. Polymers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37514492 Free PMC article.
-
Essential oils: a potential alternative with promising active ingredients for pharmaceutical formulations in chronic wound management.Inflammopharmacology. 2024 Dec;32(6):3611-3630. doi: 10.1007/s10787-024-01571-3. Epub 2024 Sep 23. Inflammopharmacology. 2024. PMID: 39312099 Review.
References
-
- Montagna W. The Structure and Function of Skin. Elsevier; Amsterdam, The Netherlands: 2012.
-
- Yousef H., Alhajj M., Sharma S. Anatomy, Skin (Integument), Epidermis, in StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing LLC; Treasure Island, FL, USA: 2022.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

