Melatonin Mitigates Drought Induced Oxidative Stress in Potato Plants through Modulation of Osmolytes, Sugar Metabolism, ABA Homeostasis and Antioxidant Enzymes
- PMID: 35567152
- PMCID: PMC9104148
- DOI: 10.3390/plants11091151
Melatonin Mitigates Drought Induced Oxidative Stress in Potato Plants through Modulation of Osmolytes, Sugar Metabolism, ABA Homeostasis and Antioxidant Enzymes
Abstract
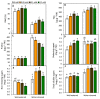
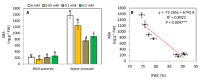
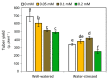
The effect of melatonin (MT) on potato plants under drought stress is still unclear in the available literature. Here, we studied the effect of MT as a foliar application at 0, 0.05, 0.1, and 0.2 mM on potato plants grown under well-watered and drought stressed conditions during the most critical period of early tuberization stage. The results indicated that under drought stress conditions, exogenous MT significantly (p ≤ 0.05) improved shoot fresh weight, shoot dry weight, chlorophyll (Chl; a, b and a + b), leaf relative water content (RWC), free amino acids (FAA), non-reducing sugars, total soluble sugars, cell membrane stability index, superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), guaiacol peroxidase (G-POX), and ascorbate peroxidase (APX) compared to the untreated plants. Meanwhile, carotenoids, proline, methylglyoxal (MG), H2O2, lipid peroxidation (malondialdehyde; MDA) and abscisic acid (ABA) were significantly decreased compared to the untreated plants. These responses may reveal the protective role of MT against drought induced carbonyl/oxidative stress and enhancing the antioxidative defense systems. Furthermore, tuber yield was differentially responded to MT treatments under well-watered and drought stressed conditions. Since, applied-MT led to an obvious decrease in tuber yield under well-watered conditions. In contrast, under drought conditions, tuber yield was substantially increased by MT-treatments up to 0.1 mM. These results may imply that under water deficiency, MT can regulate the tuberization process in potato plants by hindering ABA transport from the root to shoot system, on the one hand, and by increasing the non-reducing sugars on the other hand.
Keywords: alpha-ketoaldehyde methylglyoxal; carbonyl stress; solanum tuberosum L.; tuberization and water stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Abd El-Gawad H.G., Mukherjee S., Farag R., Abd Elbar O.H., Hikal M., Abou El-Yazied A., Abd Elhady S.A., Helal N., ElKelish A., El Nahhas N. Exogenous γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA)-induced signaling events and field performance associated with mitigation of drought stress in Phaseolus vulgaris L. Plant Signal. Behav. 2021;16:1853384. doi: 10.1080/15592324.2020.1853384. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Elkelish A., El-Mogy M.M., Niedbała G., Piekutowska M., Atia M.A., Hamada M., Shahin M., Mukherjee S., El-Yazied A.A., Shebl M. Roles of Exogenous α-Lipoic Acid and Cysteine in Mitigation of Drought Stress and Restoration of Grain Quality in Wheat. Plants. 2021;10:2318. doi: 10.3390/plants10112318. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gitz V., Meybeck A., Lipper L., Young C.D., Braatz S. Climate change and food security: Risks and responses. Food Agric. Organ. United Nations (FAO) Rep. 2016;110:2–4.
-
- Yang Z., Zhang Q., Hao X., Yue P. Changes in evapotranspiration over global semiarid regions 1984–2013. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2019;124:2946–2963. doi: 10.1029/2018JD029533. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

