SUMOylation of Dorsal attenuates Toll/NF-κB signaling
- PMID: 35567478
- PMCID: PMC9252280
- DOI: 10.1093/genetics/iyac081
SUMOylation of Dorsal attenuates Toll/NF-κB signaling
Abstract
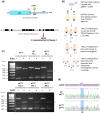
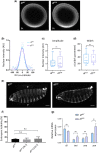
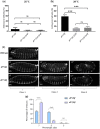
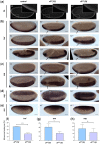
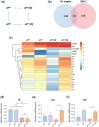
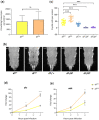
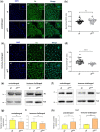
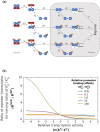
In Drosophila, Toll/NF-κB signaling plays key roles in both animal development and in host defense. The activation, intensity, and kinetics of Toll signaling are regulated by posttranslational modifications such as phosphorylation, SUMOylation, or ubiquitination that target multiple proteins in the Toll/NF-κB cascade. Here, we have generated a CRISPR-Cas9 edited Dorsal (DL) variant that is SUMO conjugation resistant. Intriguingly, embryos laid by dlSCR mothers overcome dl haploinsufficiency and complete the developmental program. This ability appears to be a result of higher transcriptional activation by DLSCR. In contrast, SUMOylation dampens DL transcriptional activation, ultimately conferring robustness to the dorso-ventral program. In the larval immune response, dlSCR animals show an increase in crystal cell numbers, stronger activation of humoral defense genes, and high cactus levels. A mathematical model that evaluates the contribution of the small fraction of SUMOylated DL (1-5%) suggests that it acts to block transcriptional activation, which is driven primarily by DL that is not SUMO conjugated. Our findings define SUMO conjugation as an important regulator of the Toll signaling cascade, in both development and host defense. Our results broadly suggest that SUMO attenuates DL at the level of transcriptional activation. Furthermore, we hypothesize that SUMO conjugation of DL may be part of a Ubc9-dependent mechanism that restrains Toll/NF-κB signaling.
Keywords: Drosophila; SUMO; haploinsufficiency; innate immunity; transcription.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Genetics Society of America.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A non-SUMOylated tax protein is still functional for NF-κB pathway activation.J Virol. 2014 Sep;88(18):10655-61. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01827-14. Epub 2014 Jul 2. J Virol. 2014. PMID: 24991007 Free PMC article.
-
Role for sumoylation in systemic inflammation and immune homeostasis in Drosophila larvae.PLoS Pathog. 2010 Dec 23;6(12):e1001234. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1001234. PLoS Pathog. 2010. PMID: 21203476 Free PMC article.
-
SUMO-Enriched Proteome for Drosophila Innate Immune Response.G3 (Bethesda). 2015 Aug 18;5(10):2137-54. doi: 10.1534/g3.115.020958. G3 (Bethesda). 2015. PMID: 26290570 Free PMC article.
-
SUMO in Drosophila Development.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;963:249-257. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-50044-7_15. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017. PMID: 28197917 Review.
-
The Drosophila Toll signaling pathway.J Immunol. 2011 Jan 15;186(2):649-56. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1002302. J Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21209287 Review.
Cited by
-
Mechanisms for controlling Dorsal nuclear levels.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024 Aug 5;12:1436369. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1436369. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024. PMID: 39161589 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SUMO3 inhibition by butyric acid suppresses cell viability and glycolysis and promotes gemcitabine antitumor activity in pancreatic cancer.Biol Direct. 2024 Aug 26;19(1):74. doi: 10.1186/s13062-024-00513-x. Biol Direct. 2024. PMID: 39183358 Free PMC article.
-
Caspar modulates primordial germ cell fate both in an Oskar-dependent and Oskar-independent manner.Biol Open. 2025 Jul 15;14(7):bio062119. doi: 10.1242/bio.062119. Epub 2025 Jul 28. Biol Open. 2025. PMID: 40614258 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

