The value of ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging scoring systems in explaining handgrip strength and functional impairment in rheumatoid arthritis patients: a pilot study
- PMID: 35567732
- PMCID: PMC9130172
- DOI: 10.1007/s11547-022-01499-0
The value of ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging scoring systems in explaining handgrip strength and functional impairment in rheumatoid arthritis patients: a pilot study
Abstract
Purpose: The goal of this study is to investigate the relationship between joint inflammation and damage of the wrists and hands, measured by semiquantitative ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging scoring systems, with functional disability and handgrip strength (HGs).
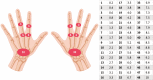
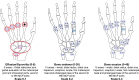
Materials and methods: Consecutive adult RA patients with active disease, as defined by a Disease Activity Score 28 joints C-reactive protein (DAS28-CRP) > 3.2, underwent a cross-sectional evaluation comprehensive of a clinimetric assessment, an HGs evaluation, an ultrasound assessment aimed at calculating the UltraSound-CLinical ARthritis Activity (US-CLARA), and a magnetic resonance imaging scored according to the modified Simplified Rheumatoid Arthritis Magnetic Resonance Imaging Score (mod SAMIS). The Spearman's rho correlation coefficient was used to test the correlations.
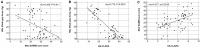
Results: Sixty-six patients with RA were investigated (age 55.6 ± 12.2 years). The mod SAMIS total score and the US-CLARA had a weak but significant correlation (rho = 0.377, p = 0.0018). Among the mod SAMIS sub-scores, there was a significant relationship between mod SAMIS bone edema (SAMIS-BME) and US-CLARA (rho = 0.799, p < 0.001) and mod SAMIS synovitis (SAMIS synovitis) and US-CLARA (rho = 0.539, p < 0.001). There were also significant negative relationships between the HGs score and the mod SAMIS total score and US-CLARA (rho = - 0.309, p = 0.011 and rho = - 0.775, p < 0.0001, respectively).
Conclusions: BME and synovitis have an influence on the function of the upper extremities. The US-CLARA and the mod SAMIS total score are intriguing options for semiquantitative assessment of joint inflammation and damage in RA.
Keywords: Disease activity; Handgrip strength; Magnetic resonance imaging; Rheumatoid arthritis; Ultrasound.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Figures

References
-
- Fiebert IM, Roach KE, Armstrong T, Mandel DW, Donohue M. Dynamometric grip strength assessment of subjects sixty year and older. Phys Occup Ther Geriatr. 1995;13:27–40. doi: 10.1080/J148v13n04_03. - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

