Health outcomes in people 2 years after surviving hospitalisation with COVID-19: a longitudinal cohort study
- PMID: 35568052
- PMCID: PMC9094732
- DOI: 10.1016/S2213-2600(22)00126-6
Health outcomes in people 2 years after surviving hospitalisation with COVID-19: a longitudinal cohort study
Abstract
Background: With the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic, growing evidence shows that a considerable proportion of people who have recovered from COVID-19 have long-term effects on multiple organs and systems. A few longitudinal studies have reported on the persistent health effects of COVID-19, but the follow-up was limited to 1 year after acute infection. The aim of our study was to characterise the longitudinal evolution of health outcomes in hospital survivors with different initial disease severity throughout 2 years after acute COVID-19 infection and to determine their recovery status.
Methods: We did an ambidirectional, longitudinal cohort study of individuals who had survived hospitalisation with COVID-19 and who had been discharged from Jin Yin-tan Hospital (Wuhan, China) between Jan 7 and May 29, 2020. We measured health outcomes 6 months (June 16-Sept 3, 2020), 12 months (Dec 16, 2020-Feb 7, 2021), and 2 years (Nov 16, 2021-Jan 10, 2022) after symptom onset with a 6-min walking distance (6MWD) test, laboratory tests, and a series of questionnaires on symptoms, mental health, health-related quality of life (HRQoL), return to work, and health-care use after discharge. A subset of COVID-19 survivors received pulmonary function tests and chest imaging at each visit. Age-matched, sex-matched, and comorbidities-matched participants without COVID-19 infection (controls) were introduced to determine the recovery status of COVID-19 survivors at 2 years. The primary outcomes included symptoms, modified British Medical Research Council (mMRC) dyspnoea scale, HRQoL, 6MWD, and return to work, and were assessed in all COVID-19 survivors who attended all three follow-up visits. Symptoms, mMRC dyspnoea scale, and HRQoL were also assessed in controls.
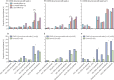
Findings: 2469 patients with COVID-19 were discharged from Jin Yin-tan Hospital between Jan 7 and May 29, 2020. 1192 COVID-19 survivors completed assessments at the three follow-up visits and were included in the final analysis, 1119 (94%) of whom attended the face-to-face interview 2 years after infection. The median age at discharge was 57·0 years (48·0-65·0) and 551 (46%) were women. The median follow-up time after symptom onset was 185·0 days (IQR 175·0-197·0) for the visit at 6 months, 349·0 days (337·0-360·0) for the visit at 12 months, and 685·0 days (675·0-698·0) for the visit at 2 years. The proportion of COVID-19 survivors with at least one sequelae symptom decreased significantly from 777 (68%) of 1149 at 6 months to 650 (55%) of 1190 at 2 years (p<0·0001), with fatigue or muscle weakness always being the most frequent. The proportion of COVID-19 survivors with an mMRC score of at least 1 was 168 (14%) of 1191 at 2 years, significantly lower than the 288 (26%) of 1104 at 6 months (p<0·0001). HRQoL continued to improve in almost all domains, especially in terms of anxiety or depression: the proportion of individuals with symptoms of anxiety or depression decreased from 256 (23%) of 1105 at 6 months to 143 (12%) 1191 at 2 years (p<0·0001). The proportion of individuals with a 6MWD less than the lower limit of the normal range declined continuously in COVID-19 survivors overall and in the three subgroups of varying initial disease severity. 438 (89%) of 494 COVID-19 survivors had returned to their original work at 2 years. Survivors with long COVID symptoms at 2 years had lower HRQoL, worse exercise capacity, more mental health abnormality, and increased health-care use after discharge than survivors without long COVID symptoms. COVID-19 survivors still had more prevalent symptoms and more problems in pain or discomfort, as well as anxiety or depression, at 2 years than did controls. Additionally, a significantly higher proportion of survivors who had received higher-level respiratory support during hospitalisation had lung diffusion impairment (43 [65%] of 66 vs 24 [36%] of 66, p=0·0009), reduced residual volume (41 [62%] vs 13 [20%], p<0·0001), and total lung capacity (26 [39%] vs four [6%], p<0·0001) than did controls.
Interpretation: Regardless of initial disease severity, COVID-19 survivors had longitudinal improvements in physical and mental health, with most returning to their original work within 2 years; however, the burden of symptomatic sequelae remained fairly high. COVID-19 survivors had a remarkably lower health status than the general population at 2 years. The study findings indicate that there is an urgent need to explore the pathogenesis of long COVID and develop effective interventions to reduce the risk of long COVID.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests We declare no competing interests.
Figures

Comment in
-
A glimpse into long COVID and symptoms - Authors' reply.Lancet Respir Med. 2022 Sep;10(9):e82. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(22)00212-0. Epub 2022 Jun 10. Lancet Respir Med. 2022. PMID: 35697052 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
A glimpse into long COVID and symptoms.Lancet Respir Med. 2022 Sep;10(9):e81. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(22)00217-X. Epub 2022 Jun 10. Lancet Respir Med. 2022. PMID: 35697054 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network. Royal College of General Practitioners COVID-19 rapid guideline: managing the long-term effects of COVID-19. Dec 18, 2020. https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng188 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

