Functional aspects of evolution in a cluster of salivary protein genes from mosquitoes
- PMID: 35568118
- PMCID: PMC9662162
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ibmb.2022.103785
Functional aspects of evolution in a cluster of salivary protein genes from mosquitoes
Abstract
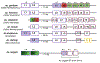
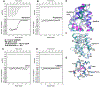
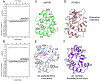
The D7 proteins are highly expressed in the saliva of hematophagous Nematocera and bind biogenic amines and eicosanoid compounds produced by the host during blood feeding. These proteins are encoded by gene clusters expressing forms having one or two odorant-binding protein-like domains. Here we examine functional diversity within the D7 group in the genus Anopheles and make structural comparisons with D7 proteins from culicine mosquitoes in order to understand aspects of D7 functional evolution. Two domain long form (D7L) and one domain short form (D7S) proteins from anopheline and culicine mosquitoes were characterized to determine their ligand selectivity and binding pocket structures. We previously showed that a D7L protein from Anopheles stephensi, of the subgenus Cellia, could bind eicosanoids at a site in its N-terminal domain but could not bind biogenic amines in its C-terminal domain as does a D7L1 ortholog from the culicine species Aedes aegypti, raising the question of whether anopheline D7L proteins had lost their ability to bind biogenic amines. Here we find that D7L from anopheline species belonging to two other subgenera, Nyssorhynchus and Anopheles, can bind biogenic amines and have a structure much like the Ae. aegypti ortholog. The unusual D7L, D7L3, can also bind serotonin in the Cellia species An. gambiae. We also show through structural comparisons with culicine forms that the biogenic amine binding function of single domain D7S proteins in the genus Anopheles may have evolved through gene conversion of structurally similar proteins, which did not have biogenic amine binding capability. Collectively, the data indicate that D7L proteins had a biogenic amine and eicosanoid binding function in the common ancestor of anopheline and culicine mosquitoes, and that the D7S proteins may have acquired a biogenic amine binding function in anophelines through a gene conversion process.
Keywords: Biogenic amine; D7 proteins; Eicosanoids; Evolution; Gene duplication; Hematophagy; Mosquito; Odorant-binding protein; Protein diversity; Saliva.
Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Adams PD, Afonine PV, Bunkoczi G, Chen VB, Davis IW, Echols N, Headd JJ, Hung LW, Kapral GJ, Grosse-Kunstleve RW, McCoy AJ, Moriarty NW, Oeffner R, Read RJ, Richardson DC, Richardson JS, Terwilliger TC, Zwart PH, 2010. PHENIX: a comprehensive Python-based system for macromolecular structure solution. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 66, 213–221. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Agarwal A, Joshi G, Nagar DP, Sharma AK, Sukumaran D, Pant SC, Parida MM, Dash PK, 2016. Mosquito saliva induced cutaneous events augment Chikungunya virus replication and disease progression. Infect Genet Evol 40, 126–135. - PubMed
-
- Almagro Armenteros JJ, Tsirigos KD, Sonderby CK, Petersen TN, Winther O, Brunak S, von Heijne G, Nielsen H, 2019. SignalP 5.0 improves signal peptide predictions using deep neural networks. Nat Biotechnol 37, 420–423. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

