Impact of COVID- 19 pandemic on antidepressants consumptions by wastewater analysis in Turkey
- PMID: 35568186
- PMCID: PMC9095074
- DOI: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.155916
Impact of COVID- 19 pandemic on antidepressants consumptions by wastewater analysis in Turkey
Abstract
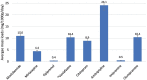
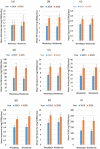
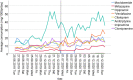
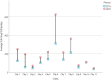
The COVID-19 pandemic has been a major challenge worldwide, forcing countries to take restrictive measures beyond conventional methods in their fight against the spread of the disease. Followingly, many studies have been conducted on the effects of these measures on mental health. Wastewater-based epidemiology (WBE) was used in this study to monitor and estimate changes in antidepressant use under normal conditions (2019) and COVID-19 pandemic conditions (2020). Likewise, this study utilized wastewater-based epidemiology (WBE) to monitor and assess changing trends from the pre-pandemic period (2019) to COVID-19 pandemic conditions in antidepressant use (2020). Wastewater samples were collected from 11 cities in Turkey throughout six sampling periods covering the pre-pandemic and during-pandemic periods (June 2019-December 2020). Then, samples were analyzed via LC-MS/MS method. As a result, we observed that venlafaxine was the drug with the highest concentration (mean ± SD: 103.6 ± 112.1 mg/1000p/day). Moreover, city number 6 presented the highest venlafaxine use and the most dramatic increase during the pandemic period. Finally, this study revealed the potential of WBE to estimate the changing trends in mental health during the ongoing pandemic.
Keywords: Antidepressants; COVID-19; Drug consumption rate changes; Wastewater-based epidemiology (WBE).
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

References
-
- Ahmed W., Angel N., Edson J., Bibby K., Bivins A., O’Brien J.W., Choi P.M., Kitajima M., Simpson S.L., Li J., Tscharke B., Verhagen R., Smith W.J.M., Zaugg J., Dierens L., Hugenholtz P., Thomas K.V., Mueller J.F. First confirmed detection of SARS-CoV-2 in untreated wastewater in Australia: a proof of concept for the wastewater surveillance of COVID-19 in the community. Sci. Total Environ. 2020;728 doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138764. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Arias-de la Torre J., Vilagut G., Ronaldson A., Serrano-Blanco A., Martín V., Peters M., Valderas J.M., Dregan A., Alonso J. Prevalence and variability of current depressive disorder in 27 European countries: a population-based study. Lancet Public Health. 2021;6:e729–e738. doi: 10.1016/S2468-2667(21)00047-5. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Been F., Emke E., Matias J., Baz-lomba J.A., Castiglioni S., Campos-mañas M., Celma A., Voogt P.De, Hernández F., Kasprzyk-hordern B., Reid M., Salgueiro-gonzález N., Steenbeek R., Nuijs A.L.N.Van, Zuccato E., Bijlsma L. Changes in drug use in European cities during early COVID-19 lockdowns - a snapshot from wastewater analysis. Environ. Int. 2021;153 doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2021.106540. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

