The antidepressant imipramine inhibits breast cancer growth by targeting estrogen receptor signaling and DNA repair events
- PMID: 35568265
- PMCID: PMC10313451
- DOI: 10.1016/j.canlet.2022.215717
The antidepressant imipramine inhibits breast cancer growth by targeting estrogen receptor signaling and DNA repair events
Abstract
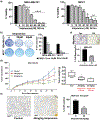
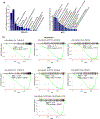
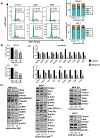
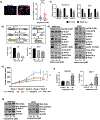
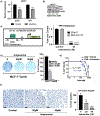
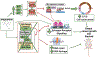
Aberrant activities of various cell cycle and DNA repair proteins promote cancer growth and progression and render them resistant to therapies. Here, we demonstrate that the anti-depressant imipramine blocks growth of triple-negative (TNBC) and estrogen receptor-positive (ER+) breast cancers by inducing cell cycle arrest and by blocking heightened homologous recombination (HR) and non-homologous end joining-mediated (NHEJ) DNA repair activities. Our results reveal that imipramine inhibits the expression of several cell cycle- and DNA repair-associated proteins including E2F1, CDK1, Cyclin D1, and RAD51. In addition, we show that imipramine inhibits the growth of ER + breast cancers by inhibiting the estrogen receptor- α (ER-α) signaling. Our studies in preclinical mouse models and ex vivo explants from breast cancer patients show that imipramine sensitizes TNBC to the PARP inhibitor olaparib and endocrine resistant ER + breast cancer to anti-estrogens. Our studies suggest that repurposing imipramine could enhance routine care for breast cancer patients. Based on these results, we designed an ongoing clinical trial, where we are testing the efficacy of imipramine for treating patients with triple-negative and estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer. Since aberrant DNA repair activity is used by many cancers to survive and become resistant to therapy, imipramine could be used alone and/or with currently used drugs for treating many aggressive cancers.
Keywords: Breast cancer; DNA damage; DNA repair; Drug repurposing; Estrogen receptor; Imipramine.
Copyright © 2022 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Inhibition of FoxM1-Mediated DNA Repair by Imipramine Blue Suppresses Breast Cancer Growth and Metastasis.Clin Cancer Res. 2016 Jul 15;22(14):3524-36. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-15-2535. Epub 2016 Feb 29. Clin Cancer Res. 2016. PMID: 26927663 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting aberrant replication and DNA repair events for treating breast cancers.Commun Biol. 2022 May 24;5(1):493. doi: 10.1038/s42003-022-03413-w. Commun Biol. 2022. PMID: 35610507 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence of Germline Mutations in Genes Engaged in DNA Damage Repair by Homologous Recombination in Patients with Triple-Negative and Hereditary Non-Triple-Negative Breast Cancers.PLoS One. 2015 Jun 17;10(6):e0130393. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0130393. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26083025 Free PMC article.
-
Homologous recombination deficiency and host anti-tumor immunity in triple-negative breast cancer.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2018 Aug;171(1):21-31. doi: 10.1007/s10549-018-4807-x. Epub 2018 May 7. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2018. PMID: 29736741 Review.
-
A DNA repair BRCA1 estrogen receptor and targeted therapy in breast cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2012 Nov 14;13(11):14898-916. doi: 10.3390/ijms131114898. Int J Mol Sci. 2012. PMID: 23203101 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Imipramine-induced Apoptosis and Metastasis Inhibition in Human Bladder Cancer T24 Cells Through EGFR/ERK/NF-κB Pathway Suppression.In Vivo. 2025 Mar-Apr;39(2):669-682. doi: 10.21873/invivo.13871. In Vivo. 2025. PMID: 40010952 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis and biological evaluation of thiourea-tethered benzodiazepinones as anti-proliferative agents targeting JAK-3 kinase.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 Aug;398(8):10667-10689. doi: 10.1007/s00210-025-03853-1. Epub 2025 Mar 3. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40029384
-
Unlocking hidden potential: advancements, approaches, and obstacles in repurposing drugs for cancer therapy.Br J Cancer. 2024 Mar;130(5):703-715. doi: 10.1038/s41416-023-02502-9. Epub 2023 Nov 27. Br J Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38012383 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Repurposing serotonergic drugs for gastric cancer: induction of apoptosis in vitro.Mol Biol Rep. 2025 Apr 9;52(1):373. doi: 10.1007/s11033-025-10474-7. Mol Biol Rep. 2025. PMID: 40202572
-
Unraveling the complex landscape of endocrine resistance in breast cancer: Emerging role of long noncoding RNA AGPG and beyond.Chin Med J (Engl). 2024 Aug 20;137(16):1985-1987. doi: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000003228. Epub 2024 Jul 19. Chin Med J (Engl). 2024. PMID: 39033392 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Society AC, Breast Cancer Facts & Figures 2019-2020, American Cancer Society, Inc, Atlanta, 2019.
-
- Waks AG, Winer EP, Breast cancer treatment: a review, JAMA 321 (3) (2019. Jan) 288–300. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

