Establishment and characterization of a new cell culture system for hepatitis B virus replication and infection
- PMID: 35568375
- PMCID: PMC9437612
- DOI: 10.1016/j.virs.2022.05.002
Establishment and characterization of a new cell culture system for hepatitis B virus replication and infection
Abstract
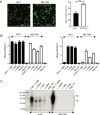
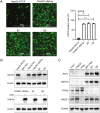
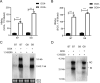
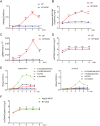
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) is a primary cause of chronic liver diseases in humans. HBV infection exhibits strict host and tissue tropism. HBV core promoter (Cp) drives transcription of pregenomic RNA (pgRNA) and plays a key role in the viral life cycle. Hepatocyte nuclear factor 4α (HNF4α) acts as a major transcriptional factor that stimulates Cp. In this work, we reported that BEL7404 cell line displayed a high efficiency of DNA transfection and high levels of HBV antigen expression after transfection of HBV replicons without prominent viral replication. The introduction of exogenous HNF4α and human sodium taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide (hNTCP) expression into BEL7404 made it permissive for HBV replication and susceptible to HBV infection. BEL7404-derived cell lines with induced HBV permissiveness and susceptibility were constructed by stable co-transfection of hNTCP and Tet-inducible HNF4α followed by limiting dilution cloning. HBV replication in such cells was sensitive to inhibition by nucleotide analog tenofovir, while the infection was inhibited by HBV entry inhibitors. This cell culture system provides a new and additional tool for the study of HBV replication and infection as well as the characterization of antiviral agents.
Keywords: BEL7404; Doxycycline (DOX); Hepatitis B virus (HBV); Hepatocyte nuclear factor 4α (HNF4α); Sodium-taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide (NTCP); Tetracycline (Tet)-On.
Copyright © 2022 The Authors. Publishing services by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Chen R., Zhu D., Ye X., Shen D., Lu R. Establishment of three human liver carcinoma cell lines and some of their biological characteristics in vitro. Sci. Sin. 1980;23:236–247. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

