Targeting the apoptosis pathway to treat tumours of the paediatric nervous system
- PMID: 35568716
- PMCID: PMC9107479
- DOI: 10.1038/s41419-022-04900-y
Targeting the apoptosis pathway to treat tumours of the paediatric nervous system
Abstract
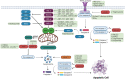
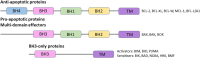
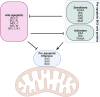
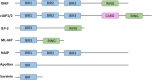
New, more effective therapeutics are required for the treatment of paediatric cancers. Current treatment protocols of cytotoxic treatments including chemotherapy trigger cancer-cell death by engaging the apoptosis pathway, and chemotherapy efficacy is frequently impeded by apoptosis dysregulation. Apoptosis dysregulation, through genetic or epigenetic mechanisms, is a feature of many cancer types, and contributes to reduced treatment response, disease progression and ultimately treatment resistance. Novel approaches are required to overcome dysregulated apoptosis signalling, increase the efficacy of cancer treatment and improve patient outcomes. Here, we provide an insight into current knowledge of how the apoptosis pathway is dysregulated in paediatric nervous system tumours, with a focus on TRAIL receptors, the BCL-2 proteins and the IAP family, and highlight preclinical evidence demonstrating that pharmacological manipulation of the apoptosis pathway can restore apoptosis signalling and sensitise cancer cells to treatment. Finally, we discuss the potential clinical implications of these findings.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Subramanian S, Ahmad T. Cancer, childhood brain tumors. StatPearls. 2018. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

