Prognostic significance of different molecular typing methods and immune status based on RNA sequencing in HR-positive and HER2-negative early-stage breast cancer
- PMID: 35568835
- PMCID: PMC9107692
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-022-09656-4
Prognostic significance of different molecular typing methods and immune status based on RNA sequencing in HR-positive and HER2-negative early-stage breast cancer
Abstract
Background: This study was conducted to evaluate the prognostic significance of different molecular typing methods and immune status based on RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) in hormone receptor (HR)-positive and human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)-negative (HR + /HER2-) early-stage breast cancer and develop a modified immunohistochemistry (IHC)-based surrogate for intrinsic subtype analysis.
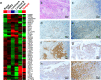
Methods: The gene expression profiles of samples from 87 HR + /HER2- early-stage breast cancer patients were evaluated using the RNA-seq of Oncotype Dx recurrence score (RS), PAM50 risk of recurrence (ROR), and immune score. Intrinsic tumor subtypes were determined using both PAM50- and IHC-based detection of estrogen receptor, progesterone receptor, Ki-67, epidermal growth factor receptor, and cytokeratins 14 and 5/6. Prognostic variables were analyzed through Cox regression analysis of disease-free survival (DFS) and distant metastasis-free survival (DMFS).
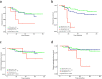
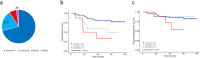
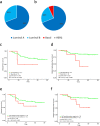
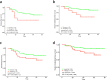
Results: Survival analysis showed that ROR better predicted recurrence and distant metastasis compared to RS (for DFS: ROR, P = 0.000; RS, P = 0.027; for DMFS, ROR, P = 0.047; RS, P = 0.621). Patients with HR + /HER2- early-stage breast cancer was classified into the luminal A, luminal B, HER2-enriched, and basal-like subtypes by PAM50. Basal-like subgroups showed the shortest DFS and DMFS. A modified IHC-based surrogate for intrinsic subtype analysis improved the concordance with PAM50 from 66.7% to 73.6%, particularly for basal-like subtype identification. High level of TILs and high expression of immune genes predicted poor prognosis. Multi-factor Cox analysis showed that IHC-based basal-like markers were the only independent factors affecting DMFS.
Conclusions: Prognosis is better evaluated by PAM50 ROR in early-stage HR + /HER2- breast cancer and significantly differs among intrinsic subtypes. The modified IHC-based subtype can improve the basal-like subtype identification of PAM50. High immunity status and IHC-based basal-like markers are negative prognostic factors.
Keywords: HR-positive/HER2-negative breast cancer; Immune rescore; Intrinsic subtype; Risk of recurrence; Tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
All authors report no conflict of interests.
Figures

References
-
- Lænkholm AV, Jensen MB, Eriksen JO, Rasmussen BB, Knoop AS, Buckingham W, Ferree S, Schaper C, Nielsen TO, Haffner T, et al. PAM50 risk of recurrence score predicts 10-year distant recurrence in a comprehensive Danish cohort of postmenopausal women allocated to 5 years of endocrine therapy for hormone receptor-positive early breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2018;36(8):735–740. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2017.74.6586. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

