m6A demethylase FTO promotes tumor progression via regulation of lipid metabolism in esophageal cancer
- PMID: 35568876
- PMCID: PMC9107638
- DOI: 10.1186/s13578-022-00798-3
m6A demethylase FTO promotes tumor progression via regulation of lipid metabolism in esophageal cancer
Abstract
Background: Epitranscriptomics studies have contributed greatly to the development of research on human cancers. In recent years, N6-methyladenosine (m6A), an RNA modification on the N-6 position of adenosine, has been found to play a potential role in epigenetic regulation. Therefore, we aimed to evaluate the regulation of cancer progression properties by m6A.
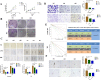
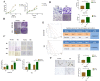
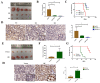
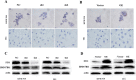
Results: We found that m6A demethylase fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO) was highly expressed in esophageal cancer (EC) stem-like cells, and that its level was also substantially increased in EC tissues, which was closely correlated with a poor prognosis in EC patients. FTO knockdown significantly inhibited the proliferation, invasion, stemness, and tumorigenicity of EC cells, whereas FTO overexpression promoted these characteristics. Furthermore, integrated transcriptome and meRIP-seq analyses revealed that HSD17B11 may be a target gene regulated by FTO. Moreover, FTO promoted the formation of lipid droplets in EC cells by enhancing HSD17B11 expression. Furthermore, depleting YTHDF1 increased the protein level of HSD17B11.
Conclusions: These data indicate that FTO may rely on the reading protein YTHDF1 to affect the translation pathway of the HSD17B11 gene to regulate the formation of lipid droplets in EC cells, thereby promoting the development of EC. The understanding of the role of epitranscriptomics in the development of EC will lay a theoretical foundation for seeking new anticancer therapies.
Keywords: Demethylase FTO; Esophageal cancer; Lipid Metabolism; m6A.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Chen S, Yang C, Wang ZW, Hu JF, Pan JJ, Liao CY, Zhang JQ, Chen JZ, Huang Y, Huang L, Zhan Q, Tian YF, Shen BY, Wang YD. CLK1/SRSF5 pathway induces aberrant exon skipping of METTL14 and Cyclin L2 and promotes growth and metastasis of pancreatic cancer. J Hematol Oncol. 2021;14:60. doi: 10.1186/s13045-021-01072-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Tan F, Zhao M, Xiong F, Wang Y, Zhang S, Gong Z, Li X, He Y, Shi L, Wang F, Xiang B, Zhou M, Li Y, Li G, Zeng Z, Xiong W, Guo C. N6-methyladenosine-dependent signalling in cancer progression and insights into cancer therapies. J Exp Clin Cancer Res: CR. 2021;40:146. doi: 10.1186/s13046-021-01952-4. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
- 82002998/national natural science foundation of china
- 82072578/national natural science foundation of china
- LHGJ20190042/medical science and technology research project in henan province
- 2021HYTP045/youth talent support project of henan province
- 21A320036/key scientific research projects in henan higher education institutions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

