Integrative analysis of multi-omics data to detect the underlying molecular mechanisms for obesity in vivo in humans
- PMID: 35568907
- PMCID: PMC9107154
- DOI: 10.1186/s40246-022-00388-x
Integrative analysis of multi-omics data to detect the underlying molecular mechanisms for obesity in vivo in humans
Abstract
Background: Obesity is a complex, multifactorial condition in which genetic play an important role. Most of the systematic studies currently focuses on individual omics aspect and provide insightful yet limited knowledge about the comprehensive and complex crosstalk between various omics levels.
Subjects and methods: Therefore, we performed a most comprehensive trans-omics study with various omics data from 104 subjects, to identify interactions/networks and particularly causal regulatory relationships within and especially those between omic molecules with the purpose to discover molecular genetic mechanisms underlying obesity etiology in vivo in humans.
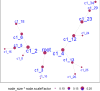
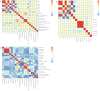
Results: By applying differentially analysis, we identified 8 differentially expressed hub genes (DEHGs), 14 differentially methylated regions (DMRs) and 12 differentially accumulated metabolites (DAMs) for obesity individually. By integrating those multi-omics biomarkers using Mendelian Randomization (MR) and network MR analyses, we identified 18 causal pathways with mediation effect. For the 20 biomarkers involved in those 18 pairs, 17 biomarkers were implicated in the pathophysiology of obesity or related diseases.
Conclusions: The integration of trans-omics and MR analyses may provide us a holistic understanding of the underlying functional mechanisms, molecular regulatory information flow and the interactive molecular systems among different omic molecules for obesity risk and other complex diseases/traits.
Keywords: Epigenomic; Genomic; Metabolomic; Multi-omics integration; Transcriptomic.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Multi-omics landscape of childhood simple obesity: novel insights into pathogenesis and biomarkers discovery.Cell Biosci. 2024 Nov 28;14(1):145. doi: 10.1186/s13578-024-01322-5. Cell Biosci. 2024. PMID: 39609876 Free PMC article.
-
From classical mendelian randomization to causal networks for systematic integration of multi-omics.Front Genet. 2022 Sep 15;13:990486. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.990486. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 36186433 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sarcoidosis Related Novel Candidate Genes Identified by Multi-Omics Integrative Analyses.OMICS. 2018 May;22(5):322-331. doi: 10.1089/omi.2018.0027. Epub 2018 Apr 24. OMICS. 2018. PMID: 29688803
-
Using empirical biological knowledge to infer regulatory networks from multi-omics data.BMC Bioinformatics. 2022 Aug 22;23(1):351. doi: 10.1186/s12859-022-04891-9. BMC Bioinformatics. 2022. PMID: 35996085 Free PMC article.
-
Integrative Analysis of Multi-omics Data for Discovery and Functional Studies of Complex Human Diseases.Adv Genet. 2016;93:147-90. doi: 10.1016/bs.adgen.2015.11.004. Epub 2016 Jan 25. Adv Genet. 2016. PMID: 26915271 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Small molecule metabolites: discovery of biomarkers and therapeutic targets.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023 Mar 20;8(1):132. doi: 10.1038/s41392-023-01399-3. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023. PMID: 36941259 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Developmental programming: Adipose depot-specific regulation of non-coding RNAs and their relation to coding RNA expression in prenatal testosterone and prenatal bisphenol-A -treated female sheep.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2023 Mar 15;564:111868. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2023.111868. Epub 2023 Jan 26. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2023. PMID: 36708980 Free PMC article.
-
The Inflammatory Mechanism of Parkinson's Disease: Gut Microbiota Metabolites Affect the Development of the Disease Through the Gut-Brain Axis.Brain Sci. 2025 Feb 6;15(2):159. doi: 10.3390/brainsci15020159. Brain Sci. 2025. PMID: 40002492 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Longitudinal multi-omics study reveals common etiology underlying association between plasma proteome and BMI trajectories in adolescent and young adult twins.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Jul 1:2023.06.28.23291995. doi: 10.1101/2023.06.28.23291995. medRxiv. 2023. Update in: BMC Med. 2023 Dec 21;21(1):508. doi: 10.1186/s12916-023-03198-7. PMID: 37425750 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
How Can We Advance Integrative Biology Research in Animal Science in 21st Century? Experience at University of Ljubljana from 2002 to 2022.OMICS. 2022 Nov;26(11):586-588. doi: 10.1089/omi.2022.0133. Epub 2022 Oct 28. OMICS. 2022. PMID: 36315198 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

