Ultrasound biomicroscopy of the equine iridocorneal angle
- PMID: 35568989
- PMCID: PMC9547819
- DOI: 10.1111/evj.13585
Ultrasound biomicroscopy of the equine iridocorneal angle
Abstract
Background: The iridocorneal angle (ICA) is the major pathway of aqueous humour outflow from the anterior chamber of the eye. Ultrasound biomicroscopy (UBM) has been utilised to characterise the morphology of this drainage pathway in numerous species. UBM may allow for early recognition of aqueous humour outflow obstructions in horses, allowing for earlier recognition of risk for glaucoma, a vision-threatening and painful disease. UBM morphology of the normal equine ICA has yet to be described.
Objectives: To determine the ultrasonographic morphology of the equine ICA by UBM in standing sedated horses.
Study design: In vivo experimental study.
Methods: Thirty healthy adult horses underwent UBM of the ICA at four locations (superior, temporal, inferior, nasal) of each eye utilising standing sedation, topical anaesthesia and auriculopalpebral perineural anaesthesia. Anatomic structures were defined on ultrasound images through comparison to published histologic photomicrographs of the equine ICA.
Results: Ultrasound imaging of the ICA at all four locations was easily performed in standing, sedated horses. High-resolution images of the ICA allowed for identification of the pectinate ligament, corneoscleral trabecular meshwork (TM), uveal TM and supraciliary TM.
Main limitations: Pupil size was midrange in all eyes, but was not strictly controlled. Lighting conditions not controlled. Various breeds included.
Conclusion: In vivo UBM of the equine ICA is feasible and provides high-resolution images of the structures of the aqueous humour outflow pathway.
Keywords: UBM; aqueous humour; eye; glaucoma; horse.
© 2022 EVJ Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

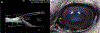

Similar articles
-
Comparison of iridocorneal angle parameters measured by spectral domain optical coherence tomography and ultrasound biomicroscopy in dogs.Vet Ophthalmol. 2022 May;25 Suppl 1:103-110. doi: 10.1111/vop.12950. Epub 2021 Nov 16. Vet Ophthalmol. 2022. PMID: 34784106
-
Corneal thickness and anterior chamber depth of the normal adult horse as measured by ultrasound biomicroscopy.Vet Ophthalmol. 2022 May;25 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):17-24. doi: 10.1111/vop.12971. Epub 2022 Jan 27. Vet Ophthalmol. 2022. PMID: 35084084 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of equine corneal disease using ultrasound biomicroscopy.Vet Ophthalmol. 2022 May;25 Suppl 1:179-184. doi: 10.1111/vop.12881. Epub 2021 Mar 11. Vet Ophthalmol. 2022. PMID: 33694251
-
Advancements in equine ophthalmic imaging enhance understanding of ocular and orbital anatomy and disease in standing sedated horses.J Am Vet Med Assoc. 2024 Oct 25;262(S2):S47-S56. doi: 10.2460/javma.24.06.0376. Print 2024 Dec 1. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 2024. PMID: 39454619 Review.
-
Ultrasound biomicroscopy in glaucoma.Surv Ophthalmol. 2011 Sep-Oct;56(5):433-50. doi: 10.1016/j.survophthal.2011.04.004. Epub 2011 Jul 23. Surv Ophthalmol. 2011. PMID: 21783220 Review.
References
-
- Annear MJ, Gemensky-Metzler AJ, Wilkie DA. Uveitic glaucoma in the horse: Equine glaucoma. Equine Vet Educ. 2012;24(2):97–105. doi:10.1111/j.2042-3292.2011.00310.x - DOI

