Localization and in silico-based functional analysis of miR-202 in bull testis
- PMID: 35569037
- PMCID: PMC9545423
- DOI: 10.1111/rda.14159
Localization and in silico-based functional analysis of miR-202 in bull testis
Abstract
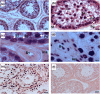
Bull fertility is pivotal to the prosperity of the cattle industry worldwide. miR-202 has been shown to be gonad specific and to have key roles in gonad function in different species. To further understand the involvement of miR-202 in bull reproduction, this study aimed to establish its localization in bovine testicular tissue and to identify putative biological functions using bioinformatics approaches. We assessed the miR-202 expression in paraffin-embedded tissue samples collected form an abattoir using in situ hybridization. miR-202 was present in Sertoli cells and in germ cells at different stages of development. Using available databases, a total of 466 predicted gene targets of miR-202 were identified. Functional annotation revealed that miR-202 target genes were mainly associated with protein modification and phosphorylation processes as well as longevity regulating pathway. Moreover, genes in the longevity regulating pathway mapped to PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway which is involved in promoting proliferation of testicular cells and spermatogenesis. These findings suggest that miR-202 plays important roles in regulating proliferation and viability of testicular cells including somatic and germ cells.
Keywords: bull; in situ hybridization; miR-202; testicular cells.
© 2022 The Authors. Reproduction in Domestic Animals published by Wiley-VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Figures


References
-
- Agarwal, V. , Bell, G. W. , Nam, J. W. , Bartel, D. P. , (2015). Predicting effective microRNA target sites in mammalian mRNAs. Elife [Internet], 4:e05005. Available from: https://elifesciences.org/articles/05005 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bannister, S. C. , Smith, C. A. , Roeszler, K. N. , Doran, T. J. , Sinclair, A. H. , & Tizard, M. L. V. (2011). Manipulation of estrogen synthesis alters MIR202* expression in embryonic chicken Gonads1. Biology of Reproduction [Internet], 85(1), 22–30. Available from: 10.1095/biolreprod.110.088476 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Barth, A. D. , Review: The use of bull breeding soundness evaluation to identify subfertile and infertile bulls. Animal [Internet]. 2018;12:s158–s164. Available from: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1751731118000538 - PubMed
-
- Bindea, G. , Mlecnik, B. , Hackl, H. , Charoentong, P. , Tosolini, M. , Kirilovsky, A. , … Galon, J. (2009). ClueGO: A Cytoscape plug‐in to decipher functionally grouped gene ontology and pathway annotation networks. Bioinformatics, 25(8), 1091–1093. Available from: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp101 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

