The Liver X Receptor Is Selectively Modulated to Differentially Alter Female Mammary Metastasis-associated Myeloid Cells
- PMID: 35569056
- PMCID: PMC9188661
- DOI: 10.1210/endocr/bqac072
The Liver X Receptor Is Selectively Modulated to Differentially Alter Female Mammary Metastasis-associated Myeloid Cells
Abstract
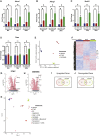
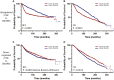
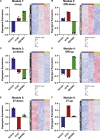
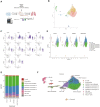
Dysregulation of cholesterol homeostasis is associated with many diseases such as cardiovascular disease and cancer. Liver X receptors (LXRs) are major upstream regulators of cholesterol homeostasis and are activated by endogenous cholesterol metabolites such as 27-hydroxycholesterol (27HC). LXRs and various LXR ligands such as 27HC have been described to influence several extra-hepatic biological systems. However, disparate reports of LXR function have emerged, especially with respect to immunology and cancer biology. This would suggest that, similar to steroid nuclear receptors, the LXRs can be selectively modulated by different ligands. Here, we use RNA-sequencing of macrophages and single-cell RNA-sequencing of immune cells from metastasis-bearing murine lungs to provide evidence that LXR satisfies the 2 principles of selective nuclear receptor modulation: (1) different LXR ligands result in overlapping but distinct gene expression profiles within the same cell type, and (2) the same LXR ligands differentially regulate gene expression in a highly context-specific manner, depending on the cell or tissue type. The concept that the LXRs can be selectively modulated provides the foundation for developing precision pharmacology LXR ligands that are tailored to promote those activities that are desirable (proimmune), but at the same time minimizing harmful side effects (such as elevated triglyceride levels).
Keywords: 27-hydroxycholesterol; SLXRM; SLiMs; breast cancer; liver X receptor; myeloid cell; nuclear receptor; selective LXR modulator.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Endocrine Society. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest and nothing to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Umetani M, Domoto H, Gormley AK, et al. 27-Hydroxycholesterol is an endogenous SERM that inhibits the cardiovascular effects of estrogen. Nat Med. 2007;13(10):1185-1192. - PubMed

