Ultrasound imaging for inguinal hernia: a pictorial review
- PMID: 35569836
- PMCID: PMC9262670
- DOI: 10.14366/usg.21192
Ultrasound imaging for inguinal hernia: a pictorial review
Abstract
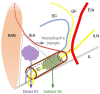
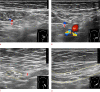
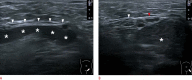
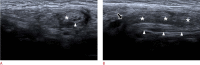
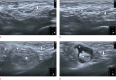
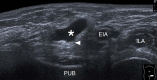
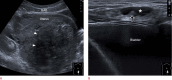
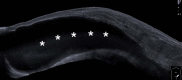
Inguinal hernia is the most prevalent type of abdominal wall hernia. Indirect inguinal hernia is twice as common as direct inguinal hernia. Computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging can be used to evaluate inguinal hernia, but these modalities are greatly limited by their cost and availability. Ultrasonography has emerged as the most convenient imaging tool for diagnosing inguinal hernia due to its advantages, such as portability and absence of radiation. The present pictorial review presents an overview on the use of ultrasonography in the evaluation of inguinal hernia with a particular emphasis on the regional anatomy, relevant scanning tips, identification of subtypes, postoperative follow-up, and diagnosis of pathologies mimicking inguinal hernia.
Keywords: Groin; Hernia recurrence; Hernia repair; Inguinal hernia; Ultrasonography.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures

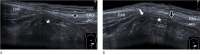


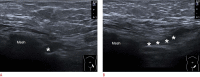
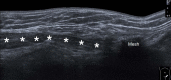
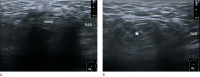
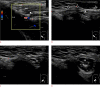
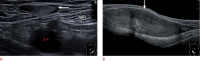
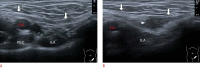
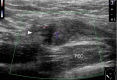


References
-
- Jacobson JA, Khoury V, Brandon CJ. Ultrasound of the groin: techniques, pathology, and pitfalls. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2015;205:513–523. - PubMed
-
- Karakousis CP. Atlas of operative procedures in surgical oncology. New York: Springer; 2015. pp. 287–295.
-
- Revzin MV, Ersahin D, Israel GM, Kirsch JD, Mathur M, Bokhari J, et al. US of the inguinal canal: comprehensive review of pathologic processes with CT and MR imaging correlation. Radiographics. 2016;36:2028–2048. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

