Toward a next-generation diagnostic tool: A review on emerging isothermal nucleic acid amplification techniques for the detection of SARS-CoV-2 and other infectious viruses
- PMID: 35569864
- PMCID: PMC8633689
- DOI: 10.1016/j.aca.2021.339338
Toward a next-generation diagnostic tool: A review on emerging isothermal nucleic acid amplification techniques for the detection of SARS-CoV-2 and other infectious viruses
Abstract
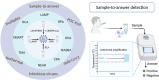
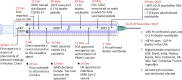
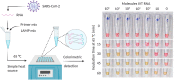
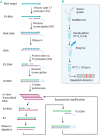
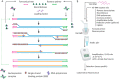
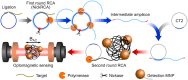
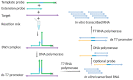
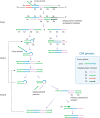
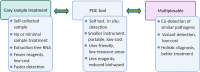
As the COVID-19 pandemic continues to affect human health across the globe rapid, simple, point-of-care (POC) diagnosis of infectious viruses such as SARS-CoV-2 remains challenging. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR)-based diagnosis has risen to meet these demands and despite its high-throughput and accuracy, it has failed to gain traction in the rapid, low-cost, point-of-test settings. In contrast, different emerging isothermal amplification-based detection methods show promise in the rapid point-of-test market. In this comprehensive study of the literature, several promising isothermal amplification methods for the detection of SARS-CoV-2 are critically reviewed that can also be applied to other infectious viruses detection. Starting with a brief discussion on the SARS-CoV-2 structure, its genomic features, and the epidemiology of the current pandemic, this review focuses on different emerging isothermal methods and their advancement. The potential of isothermal amplification combined with the revolutionary CRISPR/Cas system for a more powerful detection tool is also critically reviewed. Additionally, the commercial success of several isothermal methods in the pandemic are highlighted. Different variants of SARS-CoV-2 and their implication on isothermal amplifications are also discussed. Furthermore, three most crucial aspects in achieving a simple, fast, and multiplexable platform are addressed.
Keywords: CRISPR/Cas; Infectious viruses detection; Isothermal amplification; Pandemic; SARS-CoV-2 detection; Variants.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
There is no competing interests.
Figures








References
-
- Virus Origin/Origins of the SARS-CoV-2 Virus. https://www.who.int/health-topics/coronavirus/origins-of-the-virus
-
- Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) – World Health Organization. https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

