Association of LDL:HDL ratio with prediabetes risk: a longitudinal observational study based on Chinese adults
- PMID: 35570291
- PMCID: PMC9107720
- DOI: 10.1186/s12944-022-01655-5
Association of LDL:HDL ratio with prediabetes risk: a longitudinal observational study based on Chinese adults
Abstract
Background: Low-density lipoprotein:high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio (LDL:HDL ratio) has a good performance in identifying diabetes mellitus (DM) and insulin resistance. However, it is not yet clear whether the LDL:HDL ratio is associated with a high-risk state of prediabetes.
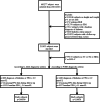
Methods: This cohort study retrospectively analyzed the data of 100,309 Chinese adults with normoglycemia at baseline. The outcome event of interest was new-onset prediabetes. Using multivariate Cox regression and smoothing splines to assess the association of LDL:HDL ratio with prediabetes.
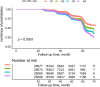
Results: During an average observation period of 37.4 months, 12,352 (12.31%) subjects were newly diagnosed with prediabetes. After adequate adjustment for important risk factors, the LDL:HDL ratio was positively correlated with the prediabetes risk, and the sensitivity analysis further suggested the robustness of the results. Additionally, in stratified analysis, we discovered significant interactions between LDL:HDL ratio and family history of DM, sex, body mass index and age (all P-interaction < 0.05); among them, the LDL:HDL ratio-related prediabetes risk decreased with the growth of body mass index and age, and increased significantly in women and people with a family history of DM.
Conclusions: The increased LDL:HDL ratio in the Chinese population indicates an increased risk of developing prediabetes, especially in women, those with a family history of DM, younger adults, and non-obese individuals.
Keywords: Chinese adults; LDL:HDL ratio; Longitudinal cohort; Prediabetes.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The author reports no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Remnant cholesterol is more positively related to diabetes, prediabetes, and insulin resistance than conventional lipid parameters and lipid ratios: A multicenter, large sample survey.J Diabetes. 2024 Aug;16(8):e13592. doi: 10.1111/1753-0407.13592. J Diabetes. 2024. PMID: 39136535 Free PMC article.
-
Association between triglyceride-to-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio and prediabetes: a cross-sectional study in Chinese non-obese people with a normal range of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol.J Transl Med. 2022 Oct 22;20(1):484. doi: 10.1186/s12967-022-03684-1. J Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 36273126 Free PMC article.
-
Triglyceride to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio is associated with regression to normoglycemia from prediabetes in adults: a 5-year cohort study in China.J Transl Med. 2023 Nov 30;21(1):868. doi: 10.1186/s12967-023-04752-w. J Transl Med. 2023. PMID: 38037094 Free PMC article.
-
The Association Between the Triglyceride-to-High-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Ratio and the Risk of Progression to Diabetes From Prediabetes: A 5-year Cohort Study in Chinese Adults.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Jul 18;13:947157. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.947157. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35923622 Free PMC article.
-
Association of Triglyceride to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio and incident of diabetes mellitus: a secondary retrospective analysis based on a Chinese cohort study.Lipids Health Dis. 2020 Mar 4;19(1):33. doi: 10.1186/s12944-020-01213-x. Lipids Health Dis. 2020. PMID: 32131838 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Remnant cholesterol for the detection of glucose metabolic states in patients with coronary heart disease angina pectoris.Acta Diabetol. 2022 Oct;59(10):1339-1347. doi: 10.1007/s00592-022-01935-7. Epub 2022 Jul 23. Acta Diabetol. 2022. PMID: 35871108
-
Remnant cholesterol is more positively related to diabetes, prediabetes, and insulin resistance than conventional lipid parameters and lipid ratios: A multicenter, large sample survey.J Diabetes. 2024 Aug;16(8):e13592. doi: 10.1111/1753-0407.13592. J Diabetes. 2024. PMID: 39136535 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced Multi-Model Machine Learning-Based Dementia Detection Using a Data Enrichment Framework: Leveraging the Blessing of Dimensionality.Bioengineering (Basel). 2025 May 30;12(6):592. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering12060592. Bioengineering (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40564409 Free PMC article.
-
The predictive value of the hs-CRP/HDL-C ratio, an inflammation-lipid composite marker, for cardiovascular disease in middle-aged and elderly people: evidence from a large national cohort study.Lipids Health Dis. 2024 Mar 1;23(1):66. doi: 10.1186/s12944-024-02055-7. Lipids Health Dis. 2024. PMID: 38429790 Free PMC article.
-
Patterns of Lipid Abnormalities in Obesity: A Comparative Analysis in Normoglycemic and Prediabetic Obese Individuals.J Pers Med. 2024 Sep 15;14(9):980. doi: 10.3390/jpm14090980. J Pers Med. 2024. PMID: 39338234 Free PMC article.
References
-
- DeFronzo RA, Ferrannini E, Zimmet P, Alberti K. International textbook of diabetes mellitus, two volume set. 4. Wiley-Blackwell; 2015.
-
- GBD 2016 Disease and Injury Incidence and Prevalence Collaborators Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 328 diseases and injuries for 195 countries, 1990–2016: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet. 2017;390(10100):1211–59. 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)32154-2. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

