Zinc and its role in vitamin D function
- PMID: 35570853
- PMCID: PMC9095729
- DOI: 10.1016/j.crphys.2022.04.001
Zinc and its role in vitamin D function
Abstract
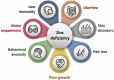
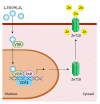
Zinc is an essential mineral with an important relationship with vitamin D. Studies have found that reduced blood zinc levels could predict vitamin D deficiency in adolescent girls, while zinc supplementation increased vitamin D levels in postmenopausal women. In vitro studies using human peritoneal macrophages have found that zinc induced the release of calcitriol (1,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol). Zinc also acts as a cofactor for vitamin D functions, as the transcriptional activity of vitamin D-dependent genes relies on zinc to exert pleiotropic functions, including mineral ion regulation. Vitamin D could also induce zinc transporters to regulate zinc homeostasis. Together, zinc and vitamin D in adequate concentrations help maintain a healthy musculoskeletal system and beyond; however, deficiency in either of these nutrients can result in various disorders affecting almost all body systems. This brief article will focus on the role of zinc in vitamin D functions.
Keywords: Deficiency; Interactions; Sources; Vitamin D; Zinc.
© 2022 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Akimbekov N.S., Ortoski R.A., Razzaque M.S. Effects of sunlight exposure and vitamin D supplementation on HIV patients. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2020;200 - PubMed
-
- Baarz B.R., Rink L. Rebalancing the unbalanced aged immune system - a special focus on zinc. Ageing Res. Rev. 2022;74 - PubMed
-
- Beigi Harchegani A., Dahan H., Tahmasbpour E., Bakhtiari Kaboutaraki H., Shahriary A. Effects of zinc deficiency on impaired spermatogenesis and male infertility: the role of oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis. Hum. Fertil. 2020;23:5–16. - PubMed
-
- Bikle D.D. In: MDText.com, Inc. Copyright © 2000-2022. (Feingold K.R., Anawalt B., Boyce A., Chrousos G., de Herder W.W., Dhatariya K., Dungan K., Hershman J.M., Hofland J., Kalra S., Kaltsas G., Koch C., Kopp P., Korbonits M., Kovacs C.S., Kuohung W., Laferrère B., Levy M., McGee E.A., McLachlan R., Morley J.E., New M., Purnell J., Sahay R., Singer F., Sperling M.A., Stratakis C.A., Trence D.L., Wilson D.P., editors. MDText.com, Inc.; South Dartmouth (MA): 2000. Vitamin D: production, metabolism and mechanisms of action. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources